版本:3cda49cfaa8556b73277ccd7e75952f0f2de2d74(Thu Jul 10 13:27:41 2025 +0200)
syzkaller 的 Executor 端也采用了分层架构,有一个控制端(下文用 Runner 来代替,其实也就是 Runner 类的功能)和多个工作端(下文用 executor 来代替),整体的工作流程如下图所示。
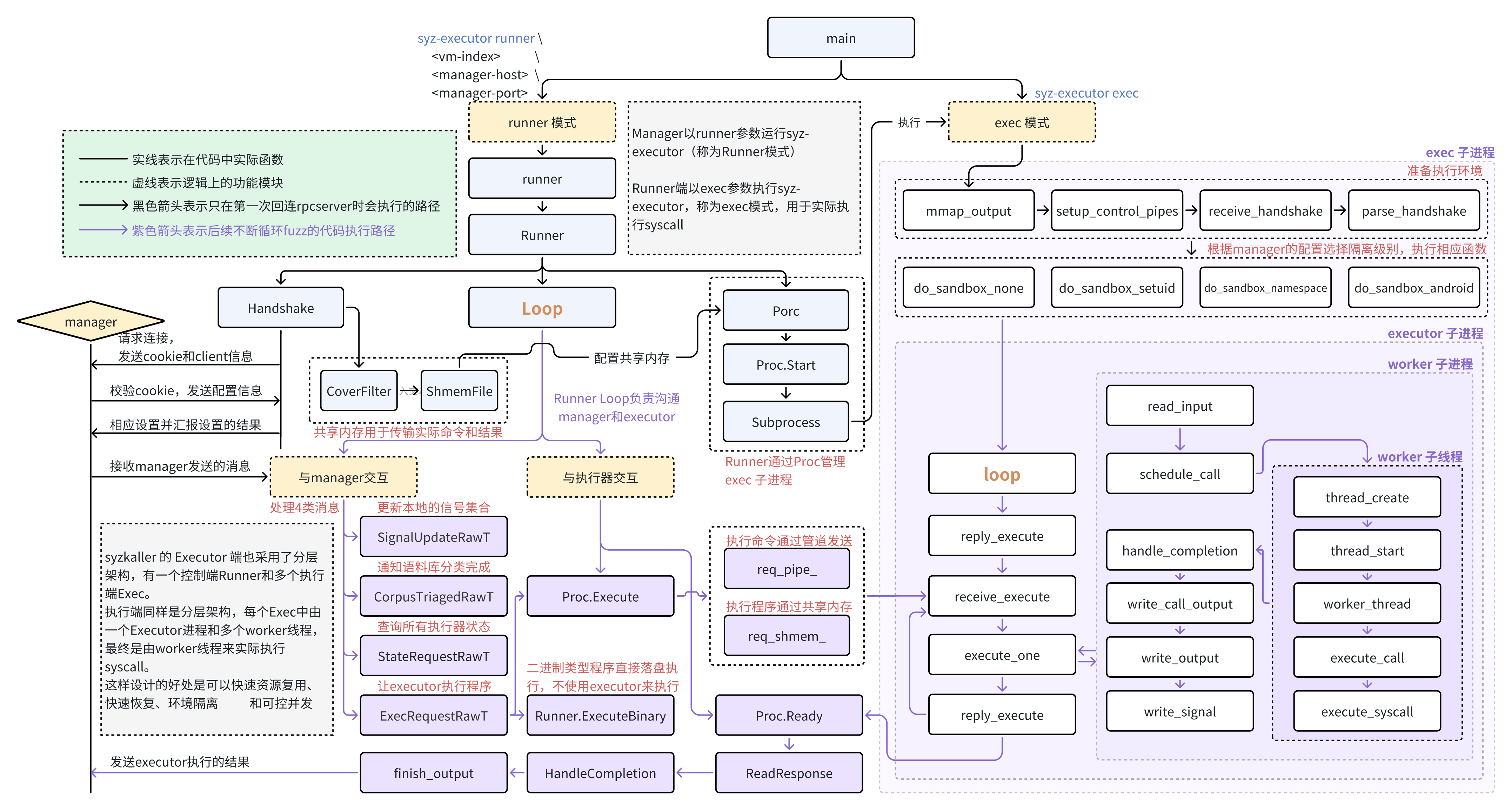
# 入口
executor 被拷贝到 vm 中后会被直接执行,入口位于 executor/executor.cc 中的 main 函数,此时 executor 的执行参数由 manager 生成,执行命令为: syz-executor runner <vm-index> <manager-host> <manager-port>
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
if (argc == 1) {
fprintf(stderr, "no command");
return 1;
}
if (strcmp(argv[1], "runner") == 0) {
runner(argv, argc); // 常规模式入口,不应该返回
fail("runner returned");
}
...
}
# 控制端 Runner
Runner 有两方面的职责,一方面,负责与 Manager 直接交互,接收 Manager 发送的各种请求,解析并完成这些请求,然后返回结果;另一方面,负责创建 executor,派发待执行的任务,收集并整理执行结果。
# 环境准备
# runner
// 这里是executor执行的入口
static void runner(char** argv, int argc)
{
if (argc != 5)
fail("usage: syz-executor runner <index> <manager-addr> <manager-port>");
char* endptr = nullptr;
int vm_index = strtol(argv[2], &endptr, 10);
if (vm_index < 0 || *endptr != 0)
failmsg("failed to parse VM index", "str='%s'", argv[2]);
const char* const manager_addr = argv[3];
const char* const manager_port = argv[4];
// 设置文件描述符上限,将进程可打开的最大 FD 数设置为 kFdLimit
struct rlimit rlim;
rlim.rlim_cur = rlim.rlim_max = kFdLimit;
if (setrlimit(RLIMIT_NOFILE, &rlim))
fail("setrlimit(RLIMIT_NOFILE) failed");
// Ignore all signals we are not interested in.
// In particular we want to ignore SIGPIPE, but also everything else since
// test processes manage to send random signals using tracepoints with bpf programs.
// This is not a bullet-proof protection, but it won't harm either.
// 信号处理策略:先“全忽略”,再精确装自己要的
for (int sig = 0; sig <= 64; sig++)
signal(sig, SIG_IGN);
if (signal(SIGINT, SigintHandler) == SIG_ERR)
fail("signal(SIGINT) failed");
if (signal(SIGTERM, SigintHandler) == SIG_ERR)
fail("signal(SIGTERM) failed");
if (signal(SIGCHLD, SigchldHandler) == SIG_ERR)
fail("signal(SIGCHLD) failed");
// 对“致命崩溃信号”安装 FatalHandler,sigaction 相比 signal 更强大,可以拿到更多上下文信息,
// 目的是把 executor 本身的崩溃变成可诊断事件,不然 fuzz 时你只看到“executor disappeared”。
struct sigaction act = {};
act.sa_flags = SA_SIGINFO;
act.sa_sigaction = FatalHandler;
for (auto sig : {SIGSEGV, SIGBUS, SIGILL, SIGFPE}) {
if (sigaction(sig, &act, nullptr))
failmsg("sigaction failed", "sig=%d", sig);
}
// 建立到 manager 的连接
Connection conn(manager_addr, manager_port);
// This is required to make Subprocess fd remapping logic work.
// kCoverFilterFd is the largest fd we set in the child processes.
//
// dup 到 kCoverFilterFd 以上,提前把连接 FD “抬高”,把低编号 FD 让出来,
// 确保后续子进程 remap 能把关键 fd 放到固定编号而不撞车。
//
// 这么做的原因是,executor 父进程会把某些重要 FD 固定映射到特定编号,
// 以便子进程里逻辑简单、无需传复杂结构,如果父进程当前已经占用了这些“目标 FD 编号”,
// 那么在 remap(比如用 dup2)时就会冲突,或者需要更复杂的避让逻辑。
for (int fd = conn.FD(); fd < kCoverFilterFd;)
fd = dup(fd);
// 启动 Runner并进入主要运行逻辑
Runner(conn, vm_index, argv[0]);
}
# Runner
Runner 是一个类,他管理一组测试子进程(Proc‘s),从 manager 接收新的测试请求,并将它们分配给子进程。
初始化阶段主要完成两件事:
- 握手:与 manager 建立连接,向 manager 报告执行环境,然后获取 manager 的配置信息并完成相关设置,并将结果返回 manager。
- 创建
Proc:根据握手阶段获取的配置信息,创建指定个子进程并完成初始化设置,这些子进程将在后续实际执行 manager 发来的程序。
Runner(Connection& conn, int vm_index, const char* bin)
: conn_(conn),
vm_index_(vm_index)
{
// 与 manager 握手,获取配置信息并初始化环境
int num_procs = Handshake();
// 构造一个“ID 池”,用于管理子进程的 proc ID 分配
proc_id_pool_.emplace(num_procs);
// 获取可选的覆盖率过滤器文件描述符
int max_signal_fd = max_signal_ ? max_signal_->FD() : -1;
int cover_filter_fd = cover_filter_ ? cover_filter_->FD() : -1;
// 创建 num_procs 个子进程 Proc 对象, 每个对象对应一个子进程,
// 创建 Proc 对象的参数会在 Handshake() 中从 manager 获取
for (int i = 0; i < num_procs; i++)
procs_.emplace_back(new Proc(conn, bin, *proc_id_pool_, restarting_, corpus_triaged_,
max_signal_fd, cover_filter_fd, use_cover_edges_, is_kernel_64_bit_, slowdown_,
syscall_timeout_ms_, program_timeout_ms_));
// 进入主循环
for (;;)
Loop();
}
# 与 Manager 握手 Handshake
int Handshake()
{
// Handshake stage 0: get a cookie from the manager.
// 阶段 0: 从连接里接收 manager 发来的 hello,hello中包含 cookie,
// 会在下一阶段用,这是一个简单的挑战/应答机制
rpc::ConnectHelloRawT conn_hello;
conn_.Recv(conn_hello);
// Handshake stage 1: share basic information about the client.
// 阶段 1: 向 manager 发送连接请求,包含 cookie 和一些客户端信息
rpc::ConnectRequestRawT conn_req;
conn_req.cookie = HashAuthCookie(conn_hello.cookie);
conn_req.id = vm_index_;
conn_req.arch = GOARCH;
conn_req.git_revision = GIT_REVISION;
conn_req.syz_revision = SYZ_REVISION;
conn_.Send(conn_req);
// manager 会回一个 ConnectReply,里面包含大量配置字段
rpc::ConnectReplyRawT conn_reply;
conn_.Recv(conn_reply);
if (conn_reply.debug)
flag_debug = true;
debug("connected to manager: procs=%d cover_edges=%d kernel_64_bit=%d slowdown=%d syscall_timeout=%u"
" program_timeout=%u features=0x%llx\n",
conn_reply.procs, conn_reply.cover_edges, conn_reply.kernel_64_bit,
conn_reply.slowdown, conn_reply.syscall_timeout_ms,
conn_reply.program_timeout_ms, static_cast<uint64>(conn_reply.features));
// 保存配置信息
leak_frames_ = conn_reply.leak_frames;
use_cover_edges_ = conn_reply.cover_edges;
is_kernel_64_bit_ = is_kernel_64_bit = conn_reply.kernel_64_bit;
slowdown_ = conn_reply.slowdown;
syscall_timeout_ms_ = conn_reply.syscall_timeout_ms;
program_timeout_ms_ = conn_reply.program_timeout_ms;
if (conn_reply.cover)
max_signal_.emplace(); // 如果 manager 要求收集覆盖率,创建覆盖率过滤器
// Handshake stage 2: share information requested by the manager.
// 阶段 2: 将 manager 请求的信息发回 manager
rpc::InfoRequestRawT info_req;
// conn_reply.files 是一组 manager 想知道的文件,executor 读取这些文件并发回文件信息
info_req.files = ReadFiles(conn_reply.files);
// This does any one-time setup for the requested features on the machine.
// Note: this can be called multiple times and must be idempotent.
#if SYZ_HAVE_FEATURES
setup_sysctl();
setup_cgroups();
#endif
#if SYZ_HAVE_SETUP_EXT
// This can be defined in common_ext.h.
setup_ext();
#endif
// 根据 features bitmask 执行特性 setup,并向 manager 汇报结果
for (const auto& feat : features) {
if (!(conn_reply.features & feat.id))
continue;
debug("setting up feature %s\n", rpc::EnumNameFeature(feat.id));
const char* reason = feat.setup();
conn_reply.features &= ~feat.id;
std::unique_ptr<rpc::FeatureInfoRawT> res(new rpc::FeatureInfoRawT);
res->id = feat.id;
res->need_setup = true;
if (reason) {
debug("failed: %s\n", reason);
res->reason = reason;
}
info_req.features.push_back(std::move(res));
}
// 对“剩余未识别 feature bit”也进行汇报
for (auto id : rpc::EnumValuesFeature()) {
if (!(conn_reply.features & id))
continue;
std::unique_ptr<rpc::FeatureInfoRawT> res(new rpc::FeatureInfoRawT);
res->id = id;
res->need_setup = false;
info_req.features.push_back(std::move(res));
}
#if SYZ_HAVE_KCSAN
// KCSAN 相关过滤器设置
setup_kcsan_filter(conn_reply.race_frames);
#endif
// 发送设置结果给 manager
conn_.Send(info_req);
rpc::InfoReplyRawT info_reply;
conn_.Recv(info_reply);
debug("received info reply: covfilter=%zu\n", info_reply.cover_filter.size());
// 如果 manager 下发了 cover_filter(一串 pc 值)
if (!info_reply.cover_filter.empty()) {
// 构造并填充 cover_filter_ 对象
cover_filter_.emplace();
// 把 pc 加入过滤集合
for (auto pc : info_reply.cover_filter)
cover_filter_->Insert(pc);
}
// 把 conn_.FD() 返回的文件描述符设置为非阻塞模式,
// 为后续“基于 pselect 的 I/O 监听/读取逻辑”做属性准备:
Select::Prepare(conn_.FD());
// 返回需要启动的子进程数量
return conn_reply.procs;
}
# CoverFilter
在握手过程中,如果 manager 要求开启覆盖率反馈,则需要初始化两个重要的 Runner 类成员变量:
max_signal_:用于记录所有已知的 signal 的合集cover_filter_:一个 “PC 集合过滤器”,决定哪些地址需要被忽略
这两个成员类型都是 std::optional<CoverFilter> , optional 表示是可选的成员, CoverFilter 是一个可放在共享内存里的 PC 集合,用于高速插入 PC 以及快速判断指定 PC 是否存在于集合。它通过 “按 PC 分段 + 分层稀疏分配 + 位图压缩” 达到:空间可控、查询快、适合跨进程共享。其具体定义和设计如下:
// CoverFilter is PC hash set that can be placed in shared memory. | |
// | |
// The set can cover up to 4 distinct 1GB regions of PCs. | |
// This restriction allows for efficient, simple and shared memory compatible representation, | |
// but should be enough to cover any reasonable combination of kernel/modules mapping. | |
// | |
// Low 3 bits of PCs are discarded. This reduces memory consumption 8x, but allows for some false positives. | |
// However, in practice false positives should be very rare. A typical coverage call instruction is 4/5 bytes, | |
// and there must be at least 1 other instruction in between them to make them different basic blocks, | |
// so it's practically impossible to place 2 of them in the same 8-byte region. | |
// For signal with hashed low 12 bits the probability is also low b/c overall density of coverage callbacks | |
// is relatively low, a KASAN Linux kernel contains 1 callback per 88 bytes of code on average. | |
// So even if we discard low 3 bits, average densitiy is still 1/11. | |
// For gVisor with dense coverage IDs special care must be taken to avoid collisions. | |
// | |
// The set is organized as a 3 level table. | |
// The top "region" level is linear lookup, but contains at most 4 entries, each covering 1GB. | |
// Most likely the first entry is the right one. This level allows to cover unconnected regions of PCs. | |
// The next "L1" level splits 1GB chunks into 1MB chunks, and allows to allocate memory only | |
// for a subset of these 1MB chunks. | |
// The last "L2" level covers 1MB chunks with 16KB bitmaps (1MB divided by 8 for 3 discarded PC bits, | |
// and divided by 8 again for 8 bits in a byte). | |
class CoverFilter | |
{ | |
public: | |
CoverFilter() | |
// 申请一片共享内存,大小 kMemSize | |
: shmem_(kMemSize), | |
// 把共享内存首地址解释成 Table 结构体指针,所以共享内存的布局就是 Table 的定义 | |
tab_(static_cast<Table*>(shmem_.Mem())) | |
{ | |
} | |
CoverFilter(int fd, void* preferred = nullptr) | |
: shmem_(fd, preferred, kMemSize, false), | |
tab_(static_cast<Table*>(shmem_.Mem())) | |
{ | |
} | |
// 把 pc 插入 filter | |
void Insert(uint64 pc) | |
{ | |
auto [byte, bit] = FindByte(pc, true); | |
byte |= bit; | |
} | |
// 检查 pc 是否在 filter 中 | |
bool Contains(uint64 pc) | |
{ | |
auto [byte, bit] = FindByte(pc, false); | |
return byte & bit; | |
} | |
// Prevents any future modifications to the filter. | |
// 只读保护,防止未来修改 | |
void Seal() | |
{ | |
shmem_.Seal(); | |
} | |
// 用于把这块共享内存传给子进程 | |
int FD() const | |
{ | |
return shmem_.FD(); | |
} | |
private: | |
static constexpr size_t kNumRegions = 4; | |
static constexpr size_t kL1Size = 1 << 30; | |
static constexpr size_t kL2Size = 1 << 20; | |
static constexpr size_t kPCDivider = 8; | |
static constexpr size_t kByteBits = 8; | |
// Approximately how much .text we can cover (2GB of PCs require 32MB shmem region). | |
static constexpr size_t kMaxCovered = 2ull << 30; | |
static constexpr size_t kCompression = kPCDivider * kByteBits; | |
static constexpr size_t kMemSize = kMaxCovered / kCompression; | |
static constexpr size_t kNoRegion = static_cast<size_t>(-1); | |
// 共享内存布局,三级表结构 | |
//regions: 每个 region 占 8 字节,存放该 region 覆盖的 1GB 地址的最高地址(低 30 位全 1) | |
//l1: 每个 region 包含 1024 个 l1 entries,每个 entries 占 2 字节,存放对应的 l2 索引 | |
//l2: 每个 l2 条目是一个 16KB bitmap,覆盖 1MB 的 PC 范围 (丢低 3 位 + 用 1bit 来表示 1byte,1MB / 8 / 8 = 16KB) | |
struct Table { | |
uint64 regions[kNumRegions]; | |
uint16 l1[kNumRegions][kL1Size / kL2Size]; | |
uint8 l2[][kL2Size / kCompression]; | |
}; | |
ShmemFile shmem_; | |
Table* tab_ = nullptr; | |
uint16 alloc_ = 0; | |
// 给定 pc 找到对应 bitmap 的 “字节引用 + bit mask” | |
std::pair<uint8&, uint8> FindByte(uint64 pc, bool add = false) | |
{ | |
static const uint8 empty = 0; | |
size_t reg = FindRegion(pc, add); | |
if (reg == kNoRegion) | |
return {const_cast<uint8&>(empty), 0}; | |
size_t l1 = (pc % kL1Size) / kL2Size; | |
size_t l2 = tab_->l1[reg][l1]; | |
if (l2 == 0) { | |
if (!add) | |
return {const_cast<uint8&>(empty), 0}; | |
l2 = ++alloc_; | |
tab_->l1[reg][l1] = l2; | |
if ((tab_->l2[l2 - 1] + 1) > reinterpret_cast<uint8*>(tab_) + kMemSize) | |
Overflow(pc); | |
} | |
size_t off = (pc % kL2Size) / kCompression; | |
size_t shift = (pc / kPCDivider) % kByteBits; | |
return {tab_->l2[l2 - 1][off], 1 << shift}; | |
} | |
// 把 PC 归类到最多 4 个 1GB 区域,返回区域索引 | |
size_t FindRegion(uint64 pc, bool add = false) | |
{ | |
const uint64 reg = pc | (kL1Size - 1); | |
for (size_t r = 0; r < kNumRegions; r++) { | |
if (tab_->regions[r] == reg) | |
return r; | |
} | |
if (!add) | |
return kNoRegion; | |
for (size_t r = 0; r < kNumRegions; r++) { | |
if (tab_->regions[r] == 0) { | |
tab_->regions[r] = reg; | |
return r; | |
} | |
} | |
Overflow(pc); | |
} | |
// 满了就直接 fail | |
NORETURN void Overflow(uint64 pc) | |
{ | |
failmsg("coverage filter is full", "pc=0x%llx regions=[0x%llx 0x%llx 0x%llx 0x%llx] alloc=%u", | |
pc, tab_->regions[0], tab_->regions[1], tab_->regions[2], tab_->regions[3], alloc_); | |
} | |
CoverFilter(const CoverFilter&) = delete; | |
CoverFilter& operator=(const CoverFilter&) = delete; | |
}; |
其中 ShmemFile 也是一个类,该类用 “临时文件 + mmap (MAP_SHARED)” 封装实现了一片共享内存,其设计目标为:
- 创建 / 映射一段可在父子进程间共享的内存;
- 通过传递
fd给子进程,让子进程mmap同一段内存; - 需要时把这段内存 “封存”(只读)以防止后续误写(
Seal())。
其定义如下:
// ShmemFile is shared memory region wrapper. | |
class ShmemFile | |
{ | |
public: | |
// Maps shared memory region of size 'size' from a new temp file. | |
// 创建一个 “匿名的、可继承 / 可传 fd 的共享内存对象”,兼容性强。 | |
ShmemFile(size_t size) | |
{ | |
// 创建一个唯一的临时文件并打开 | |
char file_name[] = "syz.XXXXXX"; | |
fd_ = mkstemp(file_name); //file_name 会被 mkstemp 改成实际文件名 | |
if (fd_ == -1) | |
failmsg("shmem open failed", "file=%s", file_name); | |
// OpenBSD has neither fallocate nor posix_fallocate. | |
// 用 ftruncate 把文件扩展到 size,作为共享内存的 backing store。 | |
if (ftruncate(fd_, size)) | |
failmsg("shmem ftruncate failed", "size=%zu", size); | |
// 映射这段文件到内存 | |
Mmap(fd_, nullptr, size, true); | |
// 马上 unlink 掉文件名, 这样的好处是: | |
// 1. 不在文件系统留下垃圾文件 | |
// 2. 生命周期由进程控制,进程结束后内核自动回收 | |
if (unlink(file_name)) | |
fail("shmem unlink failed"); | |
} | |
// Maps shared memory region from the file 'fd' in read/write or write-only mode, | |
// preferably at the address 'preferred'. | |
// 从已有 fd 直接映射共享区(attach 模式) | |
ShmemFile(int fd, void* preferred, size_t size, bool write) | |
{ | |
Mmap(fd, preferred, size, write); | |
} | |
~ShmemFile() | |
{ | |
if (munmap(mem_, size_)) | |
fail("shmem munmap failed"); | |
if (fd_ != -1) | |
close(fd_); | |
} | |
// Prevents any future modifications to the region. | |
// 把共享区变成只读,并且关闭 fd | |
void Seal() | |
{ | |
if (mprotect(mem_, size_, PROT_READ)) | |
fail("shmem mprotect failed"); | |
if (fd_ != -1) | |
close(fd_); | |
fd_ = -1; | |
} | |
int FD() const | |
{ | |
return fd_; | |
} | |
void* Mem() const | |
{ | |
return mem_; | |
} | |
private: | |
void* mem_ = nullptr; | |
size_t size_ = 0; | |
int fd_ = -1; | |
void Mmap(int fd, void* preferred, size_t size, bool write) | |
{ | |
size_ = size; | |
// MAP_SHARED:多个进程映射同一个 fd 时,看到的是同一份物理页(可共享修改) | |
mem_ = mmap(preferred, size, PROT_READ | (write ? PROT_WRITE : 0), MAP_SHARED, fd, 0); | |
if (mem_ == MAP_FAILED) | |
failmsg("shmem mmap failed", "size=%zu", size); | |
} | |
ShmemFile(const ShmemFile&) = delete; | |
ShmemFile& operator=(const ShmemFile&) = delete; | |
}; |
# 创建子进程 Proc
Proc 代表一个运行测试的子进程(使用 exec 参数重新执行 syz-executor)。他会创建用于实际执行 fuzz 任务的子进程,并通过共享内存与管道把执行请求送进去、把覆盖率 / 信号 / 结果安全地取回来。同时一个 Proc 对象是持久的,如果子进程崩溃了会重新启动子进程。
Proc(Connection& conn, const char* bin, ProcIDPool& proc_id_pool, int& restarting, const bool& corpus_triaged, int max_signal_fd, int cover_filter_fd,
bool use_cover_edges, bool is_kernel_64_bit, uint32 slowdown, uint32 syscall_timeout_ms, uint32 program_timeout_ms)
: conn_(conn),
bin_(bin),
proc_id_pool_(proc_id_pool),
id_(proc_id_pool.Alloc()),
restarting_(restarting),
corpus_triaged_(corpus_triaged),
max_signal_fd_(max_signal_fd),
cover_filter_fd_(cover_filter_fd),
use_cover_edges_(use_cover_edges),
is_kernel_64_bit_(is_kernel_64_bit),
slowdown_(slowdown),
syscall_timeout_ms_(syscall_timeout_ms),
program_timeout_ms_(program_timeout_ms),
req_shmem_(kMaxInput),
resp_shmem_(kMaxOutput),
resp_mem_(static_cast<OutputData*>(resp_shmem_.Mem()))
{
Start();
}
// 启动 syz-executor exec 子进程,并建立通信通道
void Start()
{
// 把 Proc 状态改成 Started(开始启动流程)
ChangeState(State::Started);
freshness_ = 0;
// 创建三组 pipe:请求、响应、stdout/日志
int req_pipe[2];
if (pipe(req_pipe)) // 父进程写 → 子进程读 (请求)
fail("pipe failed");
int resp_pipe[2];
if (pipe(resp_pipe)) // 子进程写 → 父进程读 (响应)
fail("pipe failed");
int stdout_pipe[2];
if (pipe(stdout_pipe)) // 子进程写 → 父进程读(stderr/log)
fail("pipe failed");
std::vector<std::pair<int, int>> fds = {
{req_pipe[0], STDIN_FILENO}, // 父进程往 req_pipe[1] 写,子进程从 stdin 读
{resp_pipe[1], STDOUT_FILENO}, // 子进程往 stdout 写结构化响应,父进程从 resp_pipe[0] 读
{stdout_pipe[1], STDERR_FILENO}, // 子进程的 debug/printf 不会污染协议 stdout,父进程从 stdout_pipe[0] 读
{req_shmem_.FD(), kInFd}, // 请求的共享内存,是一个固定 fd
{resp_shmem_.FD(), kOutFd}, // 响应的共享内存,是一个固定 fd
{max_signal_fd_, kMaxSignalFd}, // 共享的“最大信号集合”,是一个固定 fd
{cover_filter_fd_, kCoverFilterFd}, // 共享的“coverage filter”,是一个固定 fd
};
const char* argv[] = {bin_, "exec", nullptr};
process_.emplace(argv, fds); // 创建一个子进程去执行syz-executor exec
// 把 resp/stdout 的读端纳入 Select 事件循环,统一管理
Select::Prepare(resp_pipe[0]);
Select::Prepare(stdout_pipe[0]);
// 关闭不需要的端,这些端已经被子进程继承
close(req_pipe[0]);
close(resp_pipe[1]);
close(stdout_pipe[1]);
// 关闭之前的端,这些端已经过时了
close(req_pipe_);
close(resp_pipe_);
close(stdout_pipe_);
// 保存新的端
req_pipe_ = req_pipe[1];
resp_pipe_ = resp_pipe[0];
stdout_pipe_ = stdout_pipe[0];
// 如果已经有待执行消息,立刻握手
if (msg_)
Handshake();
}
# Subprocess
process_ 是一个 optional 的 Subprocess 类型的变量,负责实际创建用于执行程序的子进程,命令为: syz-executor exec 。
该类是对 posix_spawn 的最小封装,用来以严格、可控的 FD 布局和独立进程组启动一个子进程,并在需要时可靠地杀死并回收该子进程(及其可能派生的进程)。
// Subprocess allows to start and wait for a subprocess.
class Subprocess
{
public:
Subprocess(const char** argv, const std::vector<std::pair<int, int>>& fds)
{
// posix_spawn 比 fork()+dup2()+execve() 更轻量,更可控
// 用 posix_spawn_file_actions_* 系列函数来指定子进程 exec 前需要执行的动作
posix_spawn_file_actions_t actions;
// 初始化一个 空的 action 列表
if (posix_spawn_file_actions_init(&actions))
fail("posix_spawn_file_actions_init failed");
// 计算 dup2 后最大 fd, 用于避免 overlapping remap problem
int max_fd = 0;
for (auto pair : fds)
max_fd = std::max(max_fd, pair.second);
// 向 action 列表中逐项添加 dup2/close 动作,并做“必须不冲突”的硬性检查
for (auto pair : fds) {
if (pair.first != -1) {
// Remapping won't work if fd's overlap with the target range:
// we can dup something onto fd we need to dup later, in such case the later fd
// will be wrong. Resolving this would require some tricky multi-pass remapping.
// So we just require the caller to not do that.
// 如果 from_fd 落在 [0..max_fd] 这个“目标区间”里,可能出现 overlapping remap problem,
// syzkaller使用多阶段策略来避免冲突。
// 具体来说,就是预先保证所有 from_fd 都大于 max_fd,
// 这样从源到目标是“高→低”,永远不会覆盖未来要用的 fd。
if (pair.first <= max_fd)
failmsg("bad subprocess fd", "%d->%d max_fd=%d",
pair.first, pair.second, max_fd);
// dup from_fd 到 to_fd
if (posix_spawn_file_actions_adddup2(&actions, pair.first, pair.second))
fail("posix_spawn_file_actions_adddup2 failed");
} else {
// 显式关闭目标 fd
if (posix_spawn_file_actions_addclose(&actions, pair.second))
fail("posix_spawn_file_actions_addclose failed");
}
}
// 关闭多余的 fd,避免子进程继承过多无用 fd
for (int i = max_fd + 1; i < kFdLimit; i++) {
if (posix_spawn_file_actions_addclose(&actions, i))
fail("posix_spawn_file_actions_addclose failed");
}
// 设置进程组 spawn 属性
posix_spawnattr_t attr;
if (posix_spawnattr_init(&attr))
fail("posix_spawnattr_init failed");
// 指定让 exec 出来的子进程在一个新的进程组运行,同时成为该组的组长。
// 这样做的目的是方便后续对整个进程组进行管理(比如杀死整个组)。
if (posix_spawnattr_setflags(&attr, POSIX_SPAWN_SETPGROUP))
fail("posix_spawnattr_setflags failed");
// 设置子进程环境变量
const char* child_envp[] = {
// Tell ASAN to not mess with our NONFAILING and disable leak checking
// (somehow lsan is very slow in syzbot arm64 image and we are not very interested
// in leaks in the exec subprocess, it does not use malloc/new anyway).
"ASAN_OPTIONS=handle_segv=0 allow_user_segv_handler=1 detect_leaks=0",
// Disable rseq since we don't use it and we want to [ab]use it ourselves for kernel testing.
"GLIBC_TUNABLES=glibc.pthread.rseq=0",
nullptr};
// 启动子进程
if (posix_spawnp(&pid_, argv[0], &actions, &attr,
const_cast<char**>(argv), const_cast<char**>(child_envp)))
fail("posix_spawnp failed");
// 清理资源,释放 actions 和 attr 占用的资源
if (posix_spawn_file_actions_destroy(&actions))
fail("posix_spawn_file_actions_destroy failed");
if (posix_spawnattr_destroy(&attr))
fail("posix_spawnattr_destroy failed");
}
~Subprocess()
{
if (pid_)
KillAndWait();
}
int KillAndWait()
{
if (!pid_)
fail("subprocess hasn't started or already waited");
kill(pid_, SIGKILL);
int pid = 0;
int wstatus = 0;
do
pid = waitpid(pid_, &wstatus, WAIT_FLAGS);
while (pid == -1 && errno == EINTR);
if (pid != pid_)
failmsg("child wait failed", "pid_=%d pid=%d", pid_, pid);
if (WIFSTOPPED(wstatus))
failmsg("child stopped", "status=%d", wstatus);
pid_ = 0;
return ExitStatus(wstatus);
}
int WaitAndKill(uint64 timeout_ms)
{
if (!pid_)
fail("subprocess hasn't started or already waited");
uint64 start = current_time_ms();
int wstatus = 0;
for (;;) {
sleep_ms(10);
if (waitpid(pid_, &wstatus, WNOHANG | WAIT_FLAGS) == pid_)
break;
if (current_time_ms() - start > timeout_ms) {
kill(-pid_, SIGKILL); // 杀进程组
kill(pid_, SIGKILL); // 杀进程本身,防止进程组杀不干净
}
}
pid_ = 0;
return ExitStatus(wstatus);
}
private:
int pid_ = 0;
...
};
# 主循环 Loop
void Loop() | |
{ | |
Select select; | |
// 监听与 Manager 的 TCP 连接 | |
select.Arm(conn_.FD()); | |
for (auto& proc : procs_) | |
// 监听每个子进程的响应管道和输出管道 | |
proc->Arm(select); | |
// Wait for ready host connection and subprocess pipes. | |
// Timeout is for terminating hanged subprocesses. | |
select.Wait(1000); // 等待最多 1000ms(1 秒) | |
uint64 now = current_time_ms(); | |
// TCP socket 有数据可读 (manager 发来了新的请求) | |
if (select.Ready(conn_.FD())) { | |
rpc::HostMessageRawT raw; | |
// 从 socket 读取消息(阻塞直到完整消息到达) | |
conn_.Recv(raw); | |
if (auto* msg = raw.msg.AsExecRequest()) | |
Handle(*msg); // 执行请求 | |
else if (auto* msg = raw.msg.AsSignalUpdate()) | |
Handle(*msg); // 信号更新(覆盖率过滤器) | |
else if (auto* msg = raw.msg.AsCorpusTriaged()) | |
Handle(*msg); // 语料库分类完成 | |
else if (auto* msg = raw.msg.AsStateRequest()) | |
Handle(*msg); // 状态查询请求 | |
else | |
failmsg("unknown host message type", "type=%d", static_cast<int>(raw.msg.type)); | |
} | |
// 处理子进程的事件 | |
for (auto& proc : procs_) { | |
// 检查子进程状态(是否完成、是否超时、是否有输出),如果之前子进程刚创建等待握手, | |
// 则这里会检查握手是否完成,并把之前因为握手耽误的任务继续下发执行。 | |
proc->Ready(select, now, requests_.empty()); | |
// 如果有待执行的请求且子进程空闲,分配任务 | |
if (!requests_.empty()) { | |
if (proc->Execute(requests_.front())) | |
requests_.pop_front(); | |
} | |
} | |
// 健全性检查 | |
if (restarting_ < 0 || restarting_ > static_cast<int>(procs_.size())) | |
failmsg("bad restarting", "restarting=%d", restarting_); | |
} |
Select
这里简单介绍下 Select 对象,该对象封装了 Linux 的 select() 系统调用,允许同时监听多个文件描述符的可读事件。
class Select | |
{ | |
public: | |
Select() | |
{ | |
FD_ZERO(&rdset_); | |
} | |
// 告诉 Select “我关心这个 fd” | |
// 每一轮 wait 前,都会重新构造一个 Select 来监听需要关注的 fd | |
void Arm(int fd) | |
{ | |
FD_SET(fd, &rdset_); | |
max_fd_ = std::max(max_fd_, fd); | |
} | |
// 事后检查 “是哪个 fd 触发了” | |
bool Ready(int fd) const | |
{ | |
//rdset_ 会被内核修改,只保留 “已经就绪” 的 fd | |
return FD_ISSET(fd, &rdset_); | |
} | |
// 阻塞当前线程,直到有 fd 可读或超时或中断 | |
void Wait(int ms) | |
{ | |
timespec timeout = {.tv_sec = ms / 1000, .tv_nsec = (ms % 1000) * 1000 * 1000}; | |
for (;;) { | |
if (pselect(max_fd_ + 1, &rdset_, nullptr, nullptr, &timeout, nullptr) >= 0) | |
break; | |
if (errno != EINTR && errno != EAGAIN) | |
fail("pselect failed"); | |
} | |
} | |
// 把 fd 设成非阻塞(O_NONBLOCK),防止 read/write 卡住 | |
static void Prepare(int fd) | |
{ | |
if (fcntl(fd, F_SETFL, fcntl(fd, F_GETFL, 0) | O_NONBLOCK)) | |
fail("fcntl(O_NONBLOCK) failed"); | |
} | |
private: | |
fd_set rdset_; // 当前要监听的 “可读 fd 集合” | |
int max_fd_ = -1; | |
Select(const Select&) = delete; | |
Select& operator=(const Select&) = delete; | |
}; |
# manager 消息分发处理
# 执行请求 ExecRequestRawT
对应 manager 要求 executor 执行一个程序,如果:
- 二进制执行请求:直接执行
- 普通请求:分配给空闲子进程执行
void Handle(rpc::ExecRequestRawT& msg) | |
{ | |
debug("recv exec request %llu: type=%llu flags=0x%llx env=0x%llx exec=0x%llx size=%zu\n", | |
static_cast<uint64>(msg.id), | |
static_cast<uint64>(msg.type), | |
static_cast<uint64>(msg.flags), | |
static_cast<uint64>(msg.exec_opts->env_flags()), | |
static_cast<uint64>(msg.exec_opts->exec_flags()), | |
msg.data.size()); | |
// 处理二进制执行请求 | |
if (msg.type == rpc::RequestType::Binary) { | |
ExecuteBinary(msg); | |
return; | |
} | |
// 尝试将执行任务下发到子进程,轮询直到找到空闲子进程 | |
for (auto& proc : procs_) { | |
if (proc->Execute(msg)) | |
return; | |
} | |
// 所有子进程都忙,加入队列 | |
requests_.push_back(std::move(msg)); | |
} |
# 二进制执行请求
# Runner.ExecuteBinary
先通知 manager “我开始执行一个二进制任务了”→ 建一个临时工作目录 → 真正执行(在 Impl 里)并收集输出 / 错误 → 清理目录 → 把结果回传给 manager。
void ExecuteBinary(rpc::ExecRequestRawT& msg) | |
{ | |
rpc::ExecutingMessageRawT exec; | |
// 设置 id,通知 manager 这个请求开始执行 | |
exec.id = msg.id; | |
rpc::ExecutorMessageRawT raw; | |
raw.msg.Set(std::move(exec)); | |
// 立即通知 manager, 这个请求已经开始执行。 | |
conn_.Send(raw); | |
// 创建临时工作目录,并放宽权限 | |
char dir_template[] = "syz-bin-dirXXXXXX"; | |
char* dir = mkdtemp(dir_template); | |
if (dir == nullptr) | |
fail("mkdtemp failed"); | |
if (chmod(dir, 0777)) | |
fail("chmod failed"); | |
// 实际执行二进制文件,获取错误信息和输出 | |
auto [err, output] = ExecuteBinaryImpl(msg, dir); | |
// 如果 err 非空,把 errno 信息附加到 err 后面 | |
if (!err.empty()) { | |
char tmp[64]; | |
snprintf(tmp, sizeof(tmp), " (errno %d: %s)", errno, strerror(errno)); | |
err += tmp; | |
} | |
// 无论成功与否,删除临时目录 | |
remove_dir(dir); | |
// 发送执行结果给 manager | |
rpc::ExecResultRawT res; | |
res.id = msg.id; | |
res.error = std::move(err); | |
res.output = std::move(output); | |
raw.msg.Set(std::move(res)); | |
conn_.Send(raw); | |
} |
# Runner.ExecuteBinaryImpl
把 manager 发来的二进制数据落盘成可执行文件 → 用 Subprocess 启动它(stdin/stdout/stderr 重定向到管道)→ 等待它结束或超时就杀进程组 → 读取全部输出 → 返回 (error string, output bytes)。
std::tuple<std::string, std::vector<uint8_t>> ExecuteBinaryImpl(rpc::ExecRequestRawT& msg, const char* dir) | |
{ | |
// For simplicity we just wait for binary tests to complete blocking everything else. | |
// 把 msg.data 写成一个可执行文件 dir/syz-executor | |
std::string file = std::string(dir) + "/syz-executor"; | |
int fd = open(file.c_str(), O_WRONLY | O_CLOEXEC | O_CREAT, 0755); | |
if (fd == -1) | |
return {"binary file creation failed", {}}; | |
ssize_t wrote = write(fd, msg.data.data(), msg.data.size()); | |
close(fd); | |
if (wrote != static_cast<ssize_t>(msg.data.size())) | |
return {"binary file write failed", {}}; | |
// 创建管道,用于子进程的 stdin/stdout/stderr 重定向 | |
int stdin_pipe[2]; | |
if (pipe(stdin_pipe)) | |
fail("pipe failed"); | |
int stdout_pipe[2]; | |
if (pipe(stdout_pipe)) | |
fail("pipe failed"); | |
// 配置子进程参数和文件描述符重定向 | |
const char* argv[] = {file.c_str(), nullptr}; | |
std::vector<std::pair<int, int>> fds = { | |
{stdin_pipe[0], STDIN_FILENO}, | |
{stdout_pipe[1], STDOUT_FILENO}, | |
{stdout_pipe[1], STDERR_FILENO}, | |
}; | |
// 创建子进程并执行 | |
Subprocess process(argv, fds); | |
// 关闭不需要的端 | |
close(stdin_pipe[0]); | |
close(stdout_pipe[1]); | |
// 最多给 5x program timeout 时间让子进程跑完,未完就杀掉 | |
int status = process.WaitAndKill(5 * program_timeout_ms_); | |
// 读取子进程的全部输出(按 1024 字节块读) | |
std::vector<uint8_t> output; | |
for (;;) { | |
const size_t kChunk = 1024; | |
output.resize(output.size() + kChunk); | |
ssize_t n = read(stdout_pipe[0], output.data() + output.size() - kChunk, kChunk); | |
output.resize(output.size() - kChunk + std::max<ssize_t>(n, 0)); | |
if (n <= 0) | |
break; | |
} | |
close(stdin_pipe[1]); | |
close(stdout_pipe[0]); | |
return {status == kFailStatus ? "process failed" : "", std::move(output)}; | |
} | |
}; |
# 普通请求
# Proc.Execute(msg)
尝试将一个执行请求分配给当前 Proc 对象。
bool Execute(rpc::ExecRequestRawT& msg) | |
{ | |
// 检查状态:只有 Started 或 Idle 状态才能接受新请求 | |
if (state_ != State::Started && state_ != State::Idle) | |
return false; | |
// 检查 proc ID 过滤,确保请求允许使用当前 proc ID | |
if (((~msg.avoid) & proc_id_pool_.Mask()) == 0) | |
msg.avoid = 0; | |
if (msg.avoid & (1ull << id_)) | |
return false; // 请求要避开这个 proc ID | |
// 检查是否已有待处理的消息 | |
if (msg_) | |
fail("already have pending msg"); | |
// 记录等待时间 | |
if (wait_start_) | |
wait_end_ = current_time_ms(); | |
// Restart every once in a while to not let too much state accumulate. | |
// Also request if request type differs as it affects program timeout. | |
// 决定是否需要重启进程 | |
constexpr uint64 kRestartEvery = 600; | |
if (state_ == State::Idle && ((corpus_triaged_ && restarting_ == 0 && freshness_ >= kRestartEvery) || | |
req_type_ != msg.type || | |
exec_env_ != msg.exec_opts->env_flags() || sandbox_arg_ != msg.exec_opts->sandbox_arg())) | |
Restart(); // 定期重启或环境变化时重启 | |
// 保存请求并开始处理 | |
attempts_ = 0; | |
msg_ = std::move(msg); // 接管请求的所有权 | |
if (state_ == State::Started) | |
Handshake(); // 新启动的进程先握手 | |
else | |
Execute(); // 空闲进程直接执行 | |
return true; // 成功接受请求 | |
} |
# Proc.Restart
当 exec 子进程异常 / 管道写失败 / 协议乱了 / 执行挂了,它会杀掉当前子进程、收集输出、决定是否把当前请求标记失败、必要时换一个新的 proc id,然后重新 Start 一个新的 exec 子进程继续跑。
void Restart() | |
{ | |
debug("proc %d: restarting subprocess, current state %u attempts %llu\n", id_, state_, attempts_); | |
// 杀掉当前子进程并回收 | |
int status = process_->KillAndWait(); | |
// 释放 Subprocess 对象(RAII),确保 fd / 资源不再持有 | |
process_.reset(); | |
debug("proc %d: subprocess exit status %d\n", id_, status); | |
// 重启超过 20 次就视为不可恢复,收集输出并 fail | |
if (++attempts_ > 20) { | |
// 把子进程的 stdout/stderr pipe 里剩余内容尽量读干净,写入 output_ | |
while (ReadOutput()); | |
// 把 output_ 直接写到 STDERR_FILENO(父进程 stderr) | |
// 如果子进程输出里包含自己的 SYFAIL(executor 内部的失败标记), | |
// 希望它出现在我们最终 SYZFAIL 之前,便于诊断 “到底先发生了什么” | |
ssize_t wrote = write(STDERR_FILENO, output_.data(), output_.size()); | |
if (wrote != static_cast<ssize_t>(output_.size())) | |
fprintf(stderr, "output truncated: %zd/%zd (errno=%d)\n", | |
wrote, output_.size(), errno); | |
// 输出失败信息并终止,不能无限重试掩盖系统性错误 | |
uint64 req_id = msg_ ? msg_->id : -1; | |
failmsg("repeatedly failed to execute the program", "proc=%d req=%lld state=%d status=%d", | |
id_, req_id, state_, status); | |
} | |
// Ignore all other errors. | |
// Without fork server executor can legitimately exit (program contains exit_group), | |
// with fork server the top process can exit with kFailStatus if it wants special handling. | |
// 其它错误都忽略,只把 kFailStatus 当成需要特殊处理的状态 | |
if (status != kFailStatus) | |
status = 0; | |
// 决定是否 “失败当前请求”,并在需要时做收尾与上报 | |
if (FailCurrentRequest(status == kFailStatus)) { | |
// Read out all pening output until EOF. | |
// 如果请求要求返回输出,则把输出读到底 | |
if (IsSet(msg_->flags, rpc::RequestFlag::ReturnOutput)) { | |
while (ReadOutput()) | |
; | |
} | |
// 判断是否 hanged,并上报完成 | |
bool hanged = SYZ_EXECUTOR_USES_FORK_SERVER && state_ == State::Executing; | |
HandleCompletion(status, hanged); | |
if (hanged) { | |
// If the process has hanged, it may still be using per-proc resources, | |
// so allocate a fresh proc id. | |
// 如果 hang,重新分配一个新的 proc id | |
// 因为 hang 的进程可能还在使用一些与 proc id 相关的资源被占用,使用新 id 避免冲突 | |
int new_id = proc_id_pool_.Alloc(id_); | |
debug("proc %d: changing proc id to %d\n", id_, new_id); | |
id_ = new_id; | |
} | |
} else if (attempts_ > 3) // 如果不需要失败当前请求,短暂睡眠,避免疯狂重启打爆系统 | |
sleep_ms(100 * attempts_); | |
Start(); // 启动一个新的子进程 | |
} |
# Proc.Handshake
把 “这次要执行的请求 + 执行环境配置” 打包成一个固定格式的 handshake_req ,通过 req_pipe_ (也就是子进程的 stdin)写给 syz-executor exec 子进程,让它按这些参数初始化执行环境并准备开始跑。它同时推进 Proc 的状态机并记录超时计时起点;如果写 pipe 失败就认为子进程异常,立刻 Restart() 。
void Handshake() | |
{ | |
// 必须是 Started 状态且有消息 | |
if (state_ != State::Started || !msg_) | |
fail("wrong handshake state"); | |
debug("proc %d: handshaking to execute request %llu\n", id_, static_cast<uint64>(msg_->id)); | |
// 切换状态 | |
ChangeState(State::Handshaking); | |
// 记录开始时间 | |
exec_start_ = current_time_ms(); | |
// 缓存本次请求的关键字段 | |
req_type_ = msg_->type; | |
exec_env_ = msg_->exec_opts->env_flags() & ~rpc::ExecEnv::ResetState; // 把 ResetState 位清掉 | |
sandbox_arg_ = msg_->exec_opts->sandbox_arg(); | |
// 把执行配置发给 exec 子进程 | |
handshake_req req = { | |
.magic = kInMagic, | |
.use_cover_edges = use_cover_edges_, | |
.is_kernel_64_bit = is_kernel_64_bit_, | |
.flags = exec_env_, | |
.pid = static_cast<uint64>(id_), | |
.sandbox_arg = static_cast<uint64>(sandbox_arg_), | |
.syscall_timeout_ms = syscall_timeout_ms_, | |
.program_timeout_ms = ProgramTimeoutMs(), | |
.slowdown_scale = slowdown_, | |
}; | |
// 通过 req_pipe_(子进程 stdin)写入握手包;失败就重启 | |
// 子进程不可控,通信出错就重启恢复,而不是试图修补半坏状态。 | |
if (write(req_pipe_, &req, sizeof(req)) != sizeof(req)) { | |
debug("request pipe write failed (errno=%d)\n", errno); | |
Restart(); | |
} | |
} |
# Proc.Execute
Proc 的私有函数,是 Proc 真正把一个 “已分配到本 Proc 的请求 msg_” 下发给 syz-executor exec 子进程执行的入口:它会先通知 manager “我开始执行了”,然后把 program 数据放进共享内存,再通过 pipe 给子进程写一个很小的 execute_req 控制包,驱动子进程去读取共享内存并执行。
void Execute() | |
{ | |
// 只能在 Idle 且已有 msg_ 时执行 | |
if (state_ != State::Idle || !msg_) | |
fail("wrong state for execute"); | |
debug("proc %d: start executing request %llu\n", id_, static_cast<uint64>(msg_->id)); | |
// 封装执行消息 | |
rpc::ExecutingMessageRawT exec; | |
exec.id = msg_->id; | |
exec.proc_id = id_; | |
exec.try_ = attempts_; // 重试次数 | |
// 如果有等待时间统计,则填充 wait_duration 字段 | |
if (wait_start_) { | |
exec.wait_duration = (wait_end_ - wait_start_) * 1000 * 1000; | |
wait_end_ = wait_start_ = 0; | |
} | |
rpc::ExecutorMessageRawT raw; | |
raw.msg.Set(std::move(exec)); | |
conn_.Send(raw); // 通知 Manager:"我开始执行请求 XXX 了" | |
//all_call_signal 是 64-bit 位图:第 i 位 = 1 表示要收集第 i 个 syscall 的 signal | |
uint64 all_call_signal = 0; | |
//all_extra_signal 用于控制要不要从 extra 里过滤已有的 signal | |
// 为假时会把 “max_signal 里已经有的 signal” 过滤掉,extra 里只剩 “新 signal”。 | |
// 为真时则不过滤,extra 里包含所有 signal。 | |
//extra signal 是指 “非 syscall 产生的 signal”,比如背景任务、内核线程等产生的 signal。 | |
bool all_extra_signal = false; | |
// 解析 msg_->all_signal:决定 “要哪些 syscall 的 signal” | |
for (int32_t call : msg_->all_signal) { | |
// 确保 “call index 可以用 uint64 位图表达” 这个假设成立。 | |
static_assert(kMaxCalls == 64); | |
if (call < -1 || call >= static_cast<int32_t>(kMaxCalls)) | |
failmsg("bad all_signal call", "call=%d", call); | |
if (call < 0) | |
all_extra_signal = true; | |
else | |
all_call_signal |= 1ull << call; // 设置位标志 | |
} | |
// 将 program 数据写入共享内存 | |
memcpy(req_shmem_.Mem(), msg_->data.data(), std::min(msg_->data.size(), kMaxInput)); | |
// 构造执行请求结构体 | |
execute_req req{ | |
.magic = kInMagic, | |
.id = static_cast<uint64>(msg_->id), | |
.type = msg_->type, | |
.exec_flags = static_cast<uint64>(msg_->exec_opts->exec_flags()), | |
.all_call_signal = all_call_signal, | |
.all_extra_signal = all_extra_signal, | |
}; | |
// 记录开始时间,切换状态 | |
exec_start_ = current_time_ms(); | |
ChangeState(State::Executing); | |
// 通过管道发送执行命令给子进程,失败就重启 | |
if (write(req_pipe_, &req, sizeof(req)) != sizeof(req)) { | |
debug("request pipe write failed (errno=%d)\n", errno); | |
Restart(); | |
} | |
} |
到这里之后就等待子进程实际执行了,具体执行过程请看下一部分。
# 信号更新 SignalUpdateRawT
该消息代表别的 executor 发现了新的覆盖,manager 向其他 executor 同步更新。
void Handle(const rpc::SignalUpdateRawT& msg) | |
{ | |
// Manager 发现了新的覆盖率,添加到本地的 “所有信号” 集合中 | |
debug("recv signal update: new=%zu\n", msg.new_max.size()); | |
if (!max_signal_) | |
fail("signal update when no signal filter installed"); | |
for (auto pc : msg.new_max) | |
max_signal_->Insert(pc); | |
} |
# 语料库分类完成 CorpusTriagedRawT
void Handle(const rpc::CorpusTriagedRawT& msg) | |
{ | |
// TODO: repair leak checking (#4728). | |
// Manager 通知语料库分类完成,会影响是否要 restart 子进程 | |
debug("recv corpus triaged\n"); | |
corpus_triaged_ = true; | |
} |
# 状态查询 StateRequestRawT
void Handle(const rpc::StateRequestRawT& msg) | |
{ | |
// Debug request about our internal state. | |
// Manager 想知道 runner 的内部状态(调试用) | |
std::ostringstream ss; | |
ss << *this; // 输出 Runner 和所有 Proc 的状态 | |
const std::string& str = ss.str(); | |
rpc::StateResultRawT res; | |
res.data.insert(res.data.begin(), str.data(), str.data() + str.size()); | |
rpc::ExecutorMessageRawT raw; | |
raw.msg.Set(std::move(res)); | |
conn_.Send(raw); // 通过 RPC 发回 Manager | |
} |
# executor 端
Runner 中会以 exec 参数启动若干个 syz-executor 子进程,这些子进程才是实际执行 manager 发来的 program 的执行器,他们会与 Runner 通信获取待执行的任务,执行这些任务并返回覆盖率等执行信息与结果。有两种执行模式:
- snapshot 模式:
nohup syz-executor exec snapshot 1>/dev/null 2>/dev/kmsg </dev/null & - 常规模式:
syz-executor exec
# 环境准备
int main(int argc, char** argv) | |
{ | |
if (argc == 1) { | |
fprintf(stderr, "no command"); | |
return 1; | |
} | |
if (strcmp(argv[1], "runner") == 0) { | |
runner(argv, argc); // 控制端入口,不应该返回 | |
fail("runner returned"); | |
} | |
if (strcmp(argv[1], "leak") == 0) { | |
#if SYZ_HAVE_LEAK_CHECK | |
check_leaks(argv + 2, argc - 2); | |
#else | |
fail("leak checking is not implemented"); | |
#endif | |
return 0; | |
} | |
if (strcmp(argv[1], "test") == 0) | |
return run_tests(argc == 3 ? argv[2] : nullptr); | |
// 真正执行 fuzz program 的子进程入口,由 Proc::start () 启动 | |
if (strcmp(argv[1], "exec") != 0) { | |
fprintf(stderr, "unknown command"); | |
return 1; | |
} | |
// 记录启动时间 | |
start_time_ms = current_time_ms(); | |
// OS / 环境初始化,提高复现一致性 | |
os_init(argc, argv, (char*)SYZ_DATA_OFFSET, SYZ_NUM_PAGES * SYZ_PAGE_SIZE); | |
// 把工作目录切到临时目录 | |
use_temporary_dir(); | |
// 安装段错误处理函数, | |
install_segv_handler(); | |
// init_mount_image_config(); | |
//executor 内部有自己的 “线程 /worker” 结构体数组 | |
current_thread = &threads[0]; | |
//snapshot 模式 | |
if (argc > 2 && strcmp(argv[2], "snapshot") == 0) { | |
SnapshotSetup(argv, argc); | |
} else { | |
// 常规模式 | |
// 从指定的 fd 映射共享内存区域,用于接收输入,此时 runner 已经启动并 dup 好这些 fd 了 | |
// 大数据 (program) 走共享内存传输,小数据 (结构化命令) 走 pipe 传输 | |
void* mmap_out = mmap(NULL, kMaxInput, PROT_READ, MAP_SHARED, kInFd, 0); | |
if (mmap_out == MAP_FAILED) | |
fail("mmap of input file failed"); | |
//input_data 指向共享内存区域 | |
input_data = static_cast<uint8*>(mmap_out); | |
// 映射输出区域,用于存放执行结果 | |
mmap_output(kInitialOutput); | |
// Prevent test programs to mess with these fds. | |
// Due to races in collider mode, a program can e.g. ftruncate one of these fds, | |
// which will cause fuzzer to crash. | |
// 防 fuzz 过程中篡改 executor 通道 (可能会有 close ()/dup2 () 等 syscall 把 fd 搞坏) | |
close(kInFd); | |
#if !SYZ_EXECUTOR_USES_FORK_SERVER | |
// For SYZ_EXECUTOR_USES_FORK_SERVER, close(kOutFd) is invoked in the forked child, | |
// after the program has been received. | |
close(kOutFd); | |
#endif | |
// 如果 runner 提供了信号相关的 fd,则 mmap 它们并关闭原 fd | |
if (fcntl(kMaxSignalFd, F_GETFD) != -1) { // 如果 fd 没传进来会 EBADF | |
// Use random addresses for coverage filters to not collide with output_data. | |
max_signal.emplace(kMaxSignalFd, reinterpret_cast<void*>(0x110c230000ull)); | |
close(kMaxSignalFd); | |
} | |
if (fcntl(kCoverFilterFd, F_GETFD) != -1) { | |
cover_filter.emplace(kCoverFilterFd, reinterpret_cast<void*>(0x110f230000ull)); | |
close(kCoverFilterFd); | |
} | |
// 设置 runner 和 executor 的之间的控制管道 | |
setup_control_pipes(); | |
// 接收并解析 runner 的握手请求,进行初始化设置 | |
receive_handshake(); | |
#if !SYZ_EXECUTOR_USES_FORK_SERVER | |
// We receive/reply handshake when fork server is disabled just to simplify runner logic. | |
// It's a bit suboptimal, but no fork server is much slower anyway. | |
// 非 fork server 模式下:简化 runner 逻辑,先回握手再收 execute 信息并解析 | |
reply_execute(0); | |
receive_execute(); | |
#endif | |
} | |
// 覆盖率初始化(kcov):按线程开、部分预 mmap | |
if (flag_coverage) { | |
int create_count = kCoverDefaultCount, mmap_count = create_count; | |
if (flag_delay_kcov_mmap) { | |
create_count = kCoverOptimizedCount; | |
mmap_count = kCoverOptimizedPreMmap; | |
} | |
if (create_count > kMaxThreads) | |
create_count = kMaxThreads; | |
for (int i = 0; i < create_count; i++) { | |
//per-thread 的覆盖收集 | |
threads[i].cov.fd = kCoverFd + i; | |
cover_open(&threads[i].cov, false); | |
if (i < mmap_count) { | |
// Pre-mmap coverage collection for some threads. This should be enough for almost | |
// all programs, for the remaning few ones coverage will be set up when it's needed. | |
thread_mmap_cover(&threads[i]); | |
} | |
} | |
// 额外的覆盖源 | |
extra_cov.fd = kExtraCoverFd; | |
cover_open(&extra_cov, true); | |
cover_mmap(&extra_cov); | |
cover_protect(&extra_cov); | |
if (flag_extra_coverage) { | |
// Don't enable comps because we don't use them in the fuzzer yet. | |
cover_enable(&extra_cov, false, true); | |
} | |
} | |
// 选择 sandbox 执行主循环 | |
int status = 0; | |
if (flag_sandbox_none) | |
status = do_sandbox_none(); | |
#if SYZ_HAVE_SANDBOX_SETUID | |
else if (flag_sandbox_setuid) | |
status = do_sandbox_setuid(); | |
#endif | |
#if SYZ_HAVE_SANDBOX_NAMESPACE | |
else if (flag_sandbox_namespace) | |
status = do_sandbox_namespace(); | |
#endif | |
#if SYZ_HAVE_SANDBOX_ANDROID | |
else if (flag_sandbox_android) | |
status = do_sandbox_android(sandbox_arg); | |
#endif | |
else | |
fail("unknown sandbox type"); | |
// 下面的代码在正常执行流程中是不可达的 | |
#if SYZ_EXECUTOR_USES_FORK_SERVER | |
fprintf(stderr, "loop exited with status %d\n", status); | |
// If an external sandbox process wraps executor, the out pipe will be closed | |
// before the sandbox process exits this will make ipc package kill the sandbox. | |
// As the result sandbox process will exit with exit status 9 instead of the executor | |
// exit status (notably kFailStatus). So we duplicate the exit status on the pipe. | |
//fork server 模式下,退出前把状态发给 runner | |
reply_execute(status); | |
doexit(status); | |
// Unreachable. | |
return 1; | |
#else | |
// 非 fork server 模式下,直接把执行结果通过管道发给 runner | |
reply_execute(status); | |
return status; | |
#endif | |
} |
# mmap_output
把 executor 的输出缓冲区(output_data)映射到一个 “尽量不可预测、稳定” 的虚拟地址上,并支持按页扩容;输出缓冲区背后是 kOutFd 这块共享内存,Runner 另一侧会读取它解析覆盖率、signal、输出等。
static void mmap_output(uint32 size) | |
{ | |
// 如果不需要扩容就直接返回,output_size 表示当前已经映射的输出区大小 | |
if (size <= output_size) | |
return; | |
// 必须按页对齐 | |
if (size % SYZ_PAGE_SIZE != 0) | |
failmsg("trying to mmap output area that is not divisible by page size", "page=%d,area=%d", SYZ_PAGE_SIZE, size); | |
uint32* mmap_at = NULL; | |
// 第一次映射输出缓冲区 | |
if (output_data == NULL) { | |
if (kAddressSanitizer) { | |
// ASan allows user mappings only at some specific address ranges, | |
// so we don't randomize. But we also assume 64-bits and that we are running tests. | |
// 如果开了 ASan,则映射到一个固定地址(因为 ASan 只允许在特定地址映射用户内存) | |
mmap_at = (uint32*)0x7f0000000000ull; | |
} else { | |
// It's the first time we map output region - generate its location. | |
// The output region is the only thing in executor process for which consistency matters. | |
// If it is corrupted ipc package will fail to parse its contents and panic. | |
// But fuzzer constantly invents new ways of how to corrupt the region, | |
// so we map the region at a (hopefully) hard to guess address with random offset, | |
// surrounded by unmapped pages. | |
// The address chosen must also work on 32-bit kernels with 1GB user address space. | |
// 非 ASan 下挑 “难猜” 的地址来映射输出缓冲区,避免被 Fuzzer 猜到地址后篡改 | |
const uint64 kOutputBase = 0x1b2bc20000ull; | |
mmap_at = (uint32*)(kOutputBase + (1 << 20) * (getpid() % 128)); | |
} | |
} else { | |
// We are expanding the mmapped region. Adjust the parameters to avoid mmapping already | |
// mmapped area as much as possible. | |
// There exists a mremap call that could have helped, but it's purely Linux-specific. | |
// 扩容时,把新区域接在旧区域后面 | |
mmap_at = (uint32*)((char*)(output_data) + output_size); | |
} | |
// 只映射 “新增部分”,且用 MAP_FIXED 强制指定地址 | |
void* result = mmap(mmap_at, size - output_size, | |
PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED | MAP_FIXED, kOutFd, output_size); | |
if (result == MAP_FAILED || (mmap_at && result != mmap_at)) | |
failmsg("mmap of output file failed", "want %p, got %p", mmap_at, result); | |
// 第一次映射时设置 output_data 指针到共享输出区 | |
if (output_data == NULL) | |
output_data = static_cast<OutputData*>(result); | |
// 更新 output_size 为新大小 | |
output_size = size; | |
} |
# setup_control_pipes
将 Runner 预留好的控制管道绑定到对应的端上,绑定完成后,executor 和 Runner 之间就可以通过管道通信了。此时:
kInPipeFd=req_pipe[0]kOutPipeFd=reps_pipe[1]
void setup_control_pipes() | |
{ | |
// 在启动子进程时,Proc 将 req_pipe [0] 绑定到了 STDIN_FILENO | |
// 这里把 STDIN_FILENO 复制到 kInPipeFd,也即 kInPipeFd 现在也是 req_pipe [0] | |
// 所以 kInPipeFd 就是 runner 发命令给 executor 的管道读端,executor 从中读取命令 | |
// 同理 kOutPipeFd 是 executor 发结果给 runner 的管道写端,runner 从中读取结果 | |
if (dup2(0, kInPipeFd) < 0) | |
fail("dup2(0, kInPipeFd) failed"); | |
if (dup2(1, kOutPipeFd) < 0) | |
fail("dup2(1, kOutPipeFd) failed"); | |
if (dup2(2, 1) < 0) | |
fail("dup2(2, 1) failed"); | |
// We used to close(0), but now we dup stderr to stdin to keep fd numbers | |
// stable across executor and C programs generated by pkg/csource. | |
if (dup2(2, 0) < 0) | |
fail("dup2(2, 0) failed"); | |
} |
# receive_handshake
读取 Runner 发来的握手请求,根据请求内容进行初始化设置。
void receive_handshake() | |
{ | |
handshake_req req = {}; | |
// 从 kInPipeFd 读取握手请求 | |
ssize_t n = read(kInPipeFd, &req, sizeof(req)); | |
if (n != sizeof(req)) | |
failmsg("handshake read failed", "read=%zu", n); | |
// 解析握手请求,根据请求内容进行初始化设置 | |
parse_handshake(req); | |
} |
void parse_handshake(const handshake_req& req) | |
{ | |
if (req.magic != kInMagic) | |
failmsg("bad handshake magic", "magic=0x%llx", req.magic); | |
#if SYZ_HAVE_SANDBOX_ANDROID | |
sandbox_arg = req.sandbox_arg; | |
#endif | |
is_kernel_64_bit = req.is_kernel_64_bit; | |
use_cover_edges = req.use_cover_edges; | |
procid = req.pid; | |
syscall_timeout_ms = req.syscall_timeout_ms; | |
program_timeout_ms = req.program_timeout_ms; | |
slowdown_scale = req.slowdown_scale; | |
flag_debug = (bool)(req.flags & rpc::ExecEnv::Debug); | |
flag_coverage = (bool)(req.flags & rpc::ExecEnv::Signal); | |
flag_sandbox_none = (bool)(req.flags & rpc::ExecEnv::SandboxNone); | |
flag_sandbox_setuid = (bool)(req.flags & rpc::ExecEnv::SandboxSetuid); | |
flag_sandbox_namespace = (bool)(req.flags & rpc::ExecEnv::SandboxNamespace); | |
flag_sandbox_android = (bool)(req.flags & rpc::ExecEnv::SandboxAndroid); | |
flag_extra_coverage = (bool)(req.flags & rpc::ExecEnv::ExtraCover); | |
flag_net_injection = (bool)(req.flags & rpc::ExecEnv::EnableTun); | |
flag_net_devices = (bool)(req.flags & rpc::ExecEnv::EnableNetDev); | |
flag_net_reset = (bool)(req.flags & rpc::ExecEnv::EnableNetReset); | |
flag_cgroups = (bool)(req.flags & rpc::ExecEnv::EnableCgroups); | |
flag_close_fds = (bool)(req.flags & rpc::ExecEnv::EnableCloseFds); | |
flag_devlink_pci = (bool)(req.flags & rpc::ExecEnv::EnableDevlinkPCI); | |
flag_vhci_injection = (bool)(req.flags & rpc::ExecEnv::EnableVhciInjection); | |
flag_wifi = (bool)(req.flags & rpc::ExecEnv::EnableWifi); | |
flag_delay_kcov_mmap = (bool)(req.flags & rpc::ExecEnv::DelayKcovMmap); | |
flag_nic_vf = (bool)(req.flags & rpc::ExecEnv::EnableNicVF); | |
} |
然后就根据配置的沙箱的隔离级别选择不同的执行函数,执行流程大同小异,这里就直接以简单的无沙箱模式( "sandbox": "none" )来讲解流程。
# do_sandbox_none
虽然是叫做无沙箱模式,但它其实做了不少隔离 / 初始化工作:先尝试创建 PID namespace → fork → 父进程当监控者 (wait_for_loop) → 子进程成为 namespace 的 “init”(PID 1) 并做各种初始化(vhci/net/tun/wifi/tmpfs 等)→ 进入 fuzz 执行主循环 loop() 。
static int do_sandbox_none(void) | |
{ | |
// CLONE_NEWPID takes effect for the first child of the current process, | |
// so we do it before fork to make the loop "init" process of the namespace. | |
// We ought to do fail here, but sandbox=none is used in pkg/ipc tests | |
// and they are usually run under non-root. | |
// Also since debug is stripped by pkg/csource, we need to do {} | |
// even though we generally don't do {} around single statements. | |
// PID 隔离,让 loop 进程成为新 PID 命名空间的 init 进程 | |
if (unshare(CLONE_NEWPID)) { | |
debug("unshare(CLONE_NEWPID): %d\n", errno); | |
} | |
int pid = fork(); | |
if (pid != 0) | |
// 父进程 | |
return wait_for_loop(pid); | |
#if SYZ_EXECUTOR || SYZ_VHCI_INJECTION | |
//vhci 初始化 | |
initialize_vhci(); | |
#endif | |
// 通用 sandbox 初始化 | |
sandbox_common(); | |
// 丢弃 Linux capabilities,降低权限,减少 “fuzzer 以特权搞乱系统” 的情况 | |
drop_caps(); | |
#if SYZ_EXECUTOR || SYZ_NET_DEVICES | |
// 网络设备相关的早期初始化 | |
initialize_netdevices_init(); | |
#endif | |
// 创建网络命名空间 | |
if (unshare(CLONE_NEWNET)) { | |
debug("unshare(CLONE_NEWNET): %d\n", errno); | |
} | |
// Enable access to IPPROTO_ICMP sockets, must be done after CLONE_NEWNET. | |
// 让 fuzz 程序能测试 ICMP 相关路径,而不会因权限卡死 | |
write_file("/proc/sys/net/ipv4/ping_group_range", "0 65535"); | |
#if SYZ_EXECUTOR || SYZ_DEVLINK_PCI | |
// PCI 设备相关的早期初始化 | |
initialize_devlink_pci(); | |
#endif | |
#if SYZ_EXECUTOR || SYZ_NET_INJECTION | |
// TUN/TAP 设备相关的早期初始化 | |
initialize_tun(); | |
#endif | |
#if SYZ_EXECUTOR || SYZ_NET_DEVICES | |
// 创建 / 配置各种虚拟网卡 / 网络拓扑 | |
initialize_netdevices(); | |
#endif | |
#if SYZ_EXECUTOR || SYZ_WIFI | |
// WiFi 设备相关的早期初始化 | |
initialize_wifi_devices(); | |
#endif | |
// 挂 tmpfs,并 chroot 进去 | |
sandbox_common_mount_tmpfs(); | |
// 进入主循环,执行 fuzz 任务 | |
loop(); | |
doexit(1); | |
} |
# 主循环 loop
loop() 自己是 executor 的 controller(在沙箱 / 命名空间里,通常是 PID 1),每一轮它再 fork() 出一个 test worker 去跑单个 program。 loop() 进程自身是长期存活的,负责:
- 接收 runner 下发的请求
- fork 一个子进程执行
- 监控子进程是否超时 / 挂死
- 收集结果并回给 runner
每轮 fork 的子进程:只负责跑一次 program,然后 doexit(0) 。这样做的目的:隔离每次执行的副作用、便于强杀、便于复位环境、提高复现一致性。
loop 的代码位于 executor/common.h ,由于该头文件需要兼容不同的系统,所以有很多宏变量来控制编译,这里为了简化,以在 linux 上运行的默认配置来简化了代码,代码如下:
static void loop(void) | |
{ | |
// 初始化 cgroups 循环状态并对网络命名空间做 checkpoint(供后续 reset / 隔离使用)。 | |
setup_loop(); | |
// Tell parent that we are ready to serve. | |
if (!flag_snapshot) | |
reply_execute(0); // 告诉 runner “准备就绪”。 | |
int iter = 0; | |
for (;; iter++) { | |
// Create a new private work dir for this test (removed at the end of the loop). | |
// 创建一个新的工作目录用于本轮 fuzz 任务,结束后会删除该目录。 | |
char cwdbuf[32]; | |
sprintf(cwdbuf, "./%d", iter); | |
if (mkdir(cwdbuf, 0777)) | |
fail("failed to mkdir"); | |
// 重置环境,以便进行这轮 fuzz | |
// 清理当前 proc 与 /dev/loopX 的绑定 | |
// 将网络命名空间里的 iptables/arptables/ebtables 规则恢复到之前保存的基线状态 | |
reset_loop(); | |
if (!flag_snapshot) | |
receive_execute(); // 接收并解析 runner 的执行请求 | |
// 把 “执行一次 program” 隔离到子进程中进行 | |
int pid = fork(); | |
if (pid < 0) | |
fail("clone failed"); | |
if (pid == 0) { // 子进程 | |
// 进入本轮的工作目录 | |
if (chdir(cwdbuf)) | |
fail("failed to chdir"); | |
// 进行本轮的环境设置,包括进程组、资源限制、网络等 | |
setup_test(); | |
// 这两个是 loop 与 Runner 之间通信的管道,关闭防止子进程误用 | |
close(kInPipeFd); | |
close(kOutPipeFd); | |
// 执行单个 prog | |
execute_one(); | |
doexit(0); | |
} | |
debug("spawned worker pid %d\n", pid); | |
if (flag_snapshot) | |
SnapshotPrepareParent(); | |
// We used to use sigtimedwait(SIGCHLD) to wait for the subprocess. | |
// But SIGCHLD is also delivered when a process stops/continues, | |
// so it would require a loop with status analysis and timeout recalculation. | |
// SIGCHLD should also unblock the usleep below, so the spin loop | |
// should be as efficient as sigtimedwait. | |
int status = 0; | |
uint64 start = current_time_ms(); | |
uint64 last_executed = start; | |
// 通过共享内存获取子进程的执行进度 | |
uint32 executed_calls = output_data->completed.load(std::memory_order_relaxed); | |
for (;;) { | |
sleep_ms(10); | |
// 等待子进程结束,如果有其他子进程也结束顺便回收 | |
if (waitpid(-1, &status, WNOHANG | WAIT_FLAGS) == pid) | |
break; | |
// Even though the test process executes exit at the end | |
// and execution time of each syscall is bounded by syscall_timeout_ms (~50ms), | |
// this backup watchdog is necessary and its performance is important. | |
// The problem is that exit in the test processes can fail (sic). | |
// One observed scenario is that the test processes prohibits | |
// exit_group syscall using seccomp. Another observed scenario | |
// is that the test processes setups a userfaultfd for itself, | |
// then the main thread hangs when it wants to page in a page. | |
// Below we check if the test process still executes syscalls | |
// and kill it after ~1s of inactivity. | |
// (Globs are an exception: they can be slow, so we allow up to ~120s) | |
uint64 min_timeout_ms = program_timeout_ms * 3 / 5; // 最小等待时间 | |
uint64 inactive_timeout_ms = syscall_timeout_ms * 20; // 无进度超时 | |
uint64 glob_timeout_ms = program_timeout_ms * 120; // 全局硬超时 | |
uint64 now = current_time_ms(); | |
// 靠共享内存的 completed 计数判断是否还在前进 | |
uint32 now_executed = output_data->completed.load(std::memory_order_relaxed); | |
if (executed_calls != now_executed) { | |
executed_calls = now_executed; | |
last_executed = now; | |
} | |
// TODO: adjust timeout for progs with syz_usb_connect call. | |
// If the max program timeout is exceeded, kill unconditionally. | |
// 非 program 请求不看 completed 计数,因为它们不更新该计数 | |
if ((now - start > program_timeout_ms && request_type != rpc::RequestType::Glob) || (now - start > glob_timeout_ms && request_type == rpc::RequestType::Glob)) | |
goto kill_test; | |
// If the request type is not a normal test program (currently, glob expansion request), | |
// then wait for the full timeout (these requests don't update number of completed calls | |
// + they are more important and we don't want timing flakes). | |
//program 请求,先保证至少跑到 min_timeout_ms,之后若超过 inactive_timeout_ms 仍没有进度则 kill | |
if (request_type != rpc::RequestType::Program) | |
continue; | |
// Always wait at least the min timeout for each program. | |
if (now - start < min_timeout_ms) | |
continue; | |
// If it keeps completing syscalls, then don't kill it. | |
if (now - last_executed < inactive_timeout_ms) | |
continue; | |
kill_test: | |
// 一旦判定 hang,直接强杀并 wait,避免留下僵尸和资源占用。 | |
debug("killing hanging pid %d\n", pid); | |
kill_and_wait(pid, &status); | |
break; | |
} | |
//kFailStatus 视为 “执行器失败” | |
if (WEXITSTATUS(status) == kFailStatus) { | |
errno = 0; | |
fail("child failed"); | |
} | |
reply_execute(0); // 通知 runner 本轮已完成 | |
remove_dir(cwdbuf); // 删除本轮的工作目录 | |
} | |
} |
# receive_execute
从 kInPipeFd 读取 Runner 发来的执行请求,根据请求内容设置执行参数
void receive_execute() | |
{ | |
execute_req req = {}; | |
ssize_t n = 0; | |
// 从 kInPipeFd 读取执行请求 | |
while ((n = read(kInPipeFd, &req, sizeof(req))) == -1 && errno == EINTR) | |
; | |
if (n != (ssize_t)sizeof(req)) | |
failmsg("control pipe read failed", "read=%zd want=%zd", n, sizeof(req)); | |
// 解析执行请求,设置执行参数 | |
parse_execute(req); | |
} |
void parse_execute(const execute_req& req) | |
{ | |
request_id = req.id; | |
request_type = req.type; | |
flag_collect_signal = req.exec_flags & (1 << 0); | |
flag_collect_cover = req.exec_flags & (1 << 1); | |
flag_dedup_cover = req.exec_flags & (1 << 2); | |
flag_comparisons = req.exec_flags & (1 << 3); | |
flag_threaded = req.exec_flags & (1 << 4); | |
all_call_signal = req.all_call_signal; | |
all_extra_signal = req.all_extra_signal; | |
debug("[%llums] exec opts: reqid=%llu type=%llu procid=%llu threaded=%d cover=%d comps=%d dedup=%d signal=%d " | |
" sandbox=%d/%d/%d/%d timeouts=%llu/%llu/%llu kernel_64_bit=%d metadata mutation=%d\n", | |
current_time_ms() - start_time_ms, request_id, (uint64)request_type, procid, flag_threaded, flag_collect_cover, | |
flag_comparisons, flag_dedup_cover, flag_collect_signal, flag_sandbox_none, flag_sandbox_setuid, | |
flag_sandbox_namespace, flag_sandbox_android, syscall_timeout_ms, program_timeout_ms, slowdown_scale, | |
is_kernel_64_bit, flag_mutateMetadata); | |
if (syscall_timeout_ms == 0 || program_timeout_ms <= syscall_timeout_ms || slowdown_scale == 0) | |
failmsg("bad timeouts", "syscall=%llu, program=%llu, scale=%llu", | |
syscall_timeout_ms, program_timeout_ms, slowdown_scale); | |
} |
# reply_execute
向 runner 发送握手及环境准备结果, 0 表示没有错误。
void reply_execute(uint32 status) | |
{ | |
if (flag_snapshot) | |
SnapshotDone(status == kFailStatus); | |
// 向 runner 发送执行结果(握手回复) | |
if (write(kOutPipeFd, &status, sizeof(status)) != sizeof(status)) | |
fail("control pipe write failed"); | |
} |
# 执行程序 execute_one
execute_one() 是 executor 里 ** 真正 “解释并执行一条 syzkaller program(字节码)”** 的核心。它从 input_data 里按指令流读取并解析出 syscall 和 参数,将内存布置成 syscall 需要的样子,然后按照调度策略在一个或多个线程里执行 syscalls,并把结果 / 信号 / 覆盖写入共享输出区,同时用多层超时逻辑确保即便异步 syscall 卡住也能被截断并尽量产出可用反馈。
该函数代码比较长,所以也做了简化处理:
// execute_one executes program stored in input_data. | |
void execute_one() | |
{ | |
// 处理 glob 请求 | |
// Glob 请求用于在 executor 端按给定的 glob 模式安全地枚举匹配的真实文件路径(刻意规避有害符号链接和递归), | |
// 并把结果返回给上层,用于发现和构造后续 fuzz 的真实目标文件集合。 | |
if (request_type == rpc::RequestType::Glob) { | |
execute_glob(); | |
return; | |
} | |
// 除了 Glob 外必须是 Program 类型,否则协议错误直接 fail | |
if (request_type != rpc::RequestType::Program) | |
failmsg("bad request type", "type=%llu", (uint64)request_type); | |
// 设置进程名,便于调试和日志分析,格式:syz.<procid>.<request_id> | |
char buf[64]; | |
// Linux TASK_COMM_LEN is only 16, so the name needs to be compact. | |
snprintf(buf, sizeof(buf), "syz.%llu.%llu", procid, request_id); | |
prctl(PR_SET_NAME, buf); | |
if (flag_snapshot) | |
SnapshotStart(); | |
else | |
// 非 snapshot 模式,需要给本次执行准备输出缓冲区(根据需要扩容) | |
realloc_output_data(); | |
// Output buffer may be pkey-protected in snapshot mode, so don't write the output size | |
// (it's fixed and known anyway). | |
// 输出缓冲区封装器,用于后续格式化构建输出数据 | |
output_builder.emplace(output_data, output_size, !flag_snapshot); | |
uint64 start = current_time_ms(); | |
// 输入数据指针,输入数据是 syzkaller 上层构建的序列化的字节流 | |
uint8* input_pos = input_data; | |
// 准备覆盖率收集 | |
if (cover_collection_required()) { | |
if (!flag_threaded) | |
// 非 threaded 模式,直接在主线程启用 kcov | |
cover_enable(&threads[0].cov, flag_comparisons, false); | |
if (flag_extra_coverage) | |
// 额外覆盖率收集需要重置 | |
cover_reset(&extra_cov); | |
} | |
int call_index = 0; | |
uint64 prog_extra_timeout = 0; | |
uint64 prog_extra_cover_timeout = 0; | |
call_props_t call_props; | |
memset(&call_props, 0, sizeof(call_props)); | |
// 读 program 的 “指令流” 并解释执行 | |
// 第一项是 “总 call 数”,后续是指令序列,直到遇到 instr_eof 停止 | |
// | |
// 指令格式: | |
// [ header: ncalls ] | |
// [ instr tag #1 ] [ ... instr operands ... ] | |
// [ instr tag #2 ] [ ... instr operands ... ] | |
// ... | |
// [ instr_eof ] | |
read_input(&input_pos); // total number of calls | |
for (;;) { | |
//call_num 是 “指令码”,可能是 syscalls 数组中的某个 syscall 编号, | |
// 也可能是 instr_copyin/instr_copyout/instr_setprops/instr_eof 这些特殊指令 | |
uint64 call_num = read_input(&input_pos); | |
//instr_eof 指令:结束执行 | |
if (call_num == instr_eof) | |
break; | |
//instr_copyin 指令:把参数写入目标地址 | |
if (call_num == instr_copyin) { | |
// 目标写入地址 = program 里给的偏移 + SYZ_DATA_OFFSET(一个固定基址) | |
//syzkaller 把 “可写数据区” 映射到固定地址,program 用相对偏移编码地址 | |
char* addr = (char*)(read_input(&input_pos) + SYZ_DATA_OFFSET); | |
// 写入值的类型 | |
uint64 typ = read_input(&input_pos); | |
switch (typ) { | |
case arg_const: { // 写常量 | |
uint64 size, bf, bf_off, bf_len; | |
uint64 arg = read_const_arg(&input_pos, &size, &bf, &bf_off, &bf_len); | |
copyin(addr, arg, size, bf, bf_off, bf_len); | |
break; | |
} | |
case arg_addr32: | |
case arg_addr64: { // 写一个 “指针值” | |
uint64 val = read_input(&input_pos) + SYZ_DATA_OFFSET; | |
if (typ == arg_addr32) | |
NONFAILING(*(uint32*)addr = val); | |
else | |
NONFAILING(*(uint64*)addr = val); | |
break; | |
} | |
case arg_result: { // 写之前 syscall 的返回值 | |
uint64 meta = read_input(&input_pos); | |
uint64 size = meta & 0xff; | |
uint64 bf = meta >> 8; | |
uint64 val = read_result(&input_pos); | |
copyin(addr, val, size, bf, 0, 0); | |
break; | |
} | |
case arg_data: { // 写一段原始字节串 | |
uint64 size = read_input(&input_pos); | |
size &= ~(1ull << 63); // readable flag | |
if (input_pos + size > input_data + kMaxInput) | |
fail("data arg overflow"); | |
NONFAILING(memcpy(addr, input_pos, size)); | |
input_pos += size; | |
break; | |
} | |
case arg_csum: { // 计算 checksum 并写回,常用于网络协议字段,计算方式由字节流指定 | |
debug_verbose("checksum found at %p\n", addr); | |
uint64 size = read_input(&input_pos); | |
char* csum_addr = addr; | |
uint64 csum_kind = read_input(&input_pos); | |
switch (csum_kind) { | |
case arg_csum_inet: { | |
if (size != 2) | |
failmsg("bag inet checksum size", "size=%llu", size); | |
debug_verbose("calculating checksum for %p\n", csum_addr); | |
struct csum_inet csum; | |
csum_inet_init(&csum); | |
uint64 chunks_num = read_input(&input_pos); | |
uint64 chunk; | |
for (chunk = 0; chunk < chunks_num; chunk++) { | |
uint64 chunk_kind = read_input(&input_pos); | |
uint64 chunk_value = read_input(&input_pos); | |
uint64 chunk_size = read_input(&input_pos); | |
switch (chunk_kind) { | |
case arg_csum_chunk_data: | |
chunk_value += SYZ_DATA_OFFSET; | |
debug_verbose("#%lld: data chunk, addr: %llx, size: %llu\n", | |
chunk, chunk_value, chunk_size); | |
NONFAILING(csum_inet_update(&csum, (const uint8*)chunk_value, chunk_size)); | |
break; | |
case arg_csum_chunk_const: | |
if (chunk_size != 2 && chunk_size != 4 && chunk_size != 8) | |
failmsg("bad checksum const chunk size", "size=%lld", chunk_size); | |
// Here we assume that const values come to us big endian. | |
debug_verbose("#%lld: const chunk, value: %llx, size: %llu\n", | |
chunk, chunk_value, chunk_size); | |
csum_inet_update(&csum, (const uint8*)&chunk_value, chunk_size); | |
break; | |
default: | |
failmsg("bad checksum chunk kind", "kind=%llu", chunk_kind); | |
} | |
} | |
uint16 csum_value = csum_inet_digest(&csum); | |
debug_verbose("writing inet checksum %hx to %p\n", csum_value, csum_addr); | |
copyin(csum_addr, csum_value, 2, binary_format_native, 0, 0); | |
break; | |
} | |
default: | |
failmsg("bad checksum kind", "kind=%llu", csum_kind); | |
} | |
break; | |
} | |
default: | |
failmsg("bad argument type", "type=%llu", typ); | |
} | |
continue; | |
} | |
// 声明 “要从某地址读回输出”,但不立刻做 | |
// 某次 syscall 完成后,从指定地址读出 size 字节放到 output,便于后续引用 | |
if (call_num == instr_copyout) { | |
read_input(&input_pos); // index | |
read_input(&input_pos); // addr | |
read_input(&input_pos); // size | |
// The copyout will happen when/if the call completes. | |
continue; | |
} | |
// 设置 syscall 执行属性 | |
if (call_num == instr_setprops) { | |
read_call_props_t(call_props, read_input(&input_pos, false)); | |
continue; | |
} | |
// 正常 syscall:解析参数 → schedule → 执行 / 等待 → completion | |
if (call_num >= ARRAY_SIZE(syscalls)) | |
failmsg("invalid syscall number", "call_num=%llu", call_num); | |
const call_t* call = &syscalls[call_num]; | |
// 某些 syscall 本身需要更长 program 超时 | |
if (prog_extra_timeout < call->attrs.prog_timeout) | |
prog_extra_timeout = call->attrs.prog_timeout * slowdown_scale; | |
// 需要额外时间写 remote coverage | |
if (call->attrs.remote_cover) | |
prog_extra_cover_timeout = 500 * slowdown_scale; // 500 ms | |
//copyout_index 与前面 instr_copyout 对应,表示该 call 完成后要做哪些 copyout。 | |
uint64 copyout_index = read_input(&input_pos); | |
// 读参数 | |
uint64 num_args = read_input(&input_pos); | |
if (num_args > kMaxArgs) | |
failmsg("command has bad number of arguments", "args=%llu", num_args); | |
uint64 args[kMaxArgs] = {}; | |
// 根据不同参数类型解析参数,形成最终 syscall 参数值 | |
for (uint64 i = 0; i < num_args; i++) | |
args[i] = read_arg(&input_pos); | |
for (uint64 i = num_args; i < kMaxArgs; i++) | |
args[i] = 0; | |
// 把这个 call 分配到某个线程 th 去执行 | |
thread_t* th = schedule_call(call_index++, call_num, copyout_index, | |
num_args, args, input_pos, call_props); | |
// 根据 call_props 决定是否等待 call 完成 | |
if (call_props.async && flag_threaded) { | |
// Don't wait for an async call to finish. We'll wait at the end. | |
// If we're not in the threaded mode, just ignore the async flag - during repro simplification syzkaller | |
// will anyway try to make it non-threaded. | |
} else if (flag_threaded) { | |
// Wait for call completion. | |
uint64 timeout_ms = syscall_timeout_ms + call->attrs.timeout * slowdown_scale; | |
// This is because of printing pre/post call. Ideally we print everything in the main thread | |
// and then remove this (would also avoid intermixed output). | |
if (flag_debug && timeout_ms < 1000) | |
timeout_ms = 1000; | |
// 等该线程的 syscall 完成或超时 | |
if (event_timedwait(&th->done, timeout_ms)) | |
handle_completion(th); | |
// Check if any of previous calls have completed. | |
// 遍历所有线程,发现 “已经完成但还没处理 completion” 的,就处理掉。 | |
// 避免 output 写入延迟累积、也避免 completed 计数不更新导致外层误判 hang | |
for (int i = 0; i < kMaxThreads; i++) { | |
th = &threads[i]; | |
if (th->executing && event_isset(&th->done)) | |
handle_completion(th); | |
} | |
} else { | |
// Execute directly. | |
// 非 threaded 模式,在主线程直接执行 | |
if (th != &threads[0]) | |
fail("using non-main thread in non-thread mode"); | |
event_reset(&th->ready); // 重置 ready 事件,准备执行 | |
execute_call(th); // 直接执行 syscall | |
event_set(&th->done); // 标记完成 | |
handle_completion(th); // 完成后的处理 | |
} | |
memset(&call_props, 0, sizeof(call_props)); // 清空 call_props,避免影响下一个 call | |
} | |
// 循环结束,如果还有未完成的 syscall,则等待它们完成或超时 | |
if (running > 0) { | |
// Give unfinished syscalls some additional time. | |
last_scheduled = 0; | |
uint64 wait_start = current_time_ms(); | |
uint64 wait_end = wait_start + 2 * syscall_timeout_ms; | |
wait_end = std::max(wait_end, start + program_timeout_ms / 6); | |
wait_end = std::max(wait_end, wait_start + prog_extra_timeout); | |
while (running > 0 && current_time_ms() <= wait_end) { | |
sleep_ms(1 * slowdown_scale); | |
// 处理已经完成的 syscall | |
for (int i = 0; i < kMaxThreads; i++) { | |
thread_t* th = &threads[i]; | |
if (th->executing && event_isset(&th->done)) | |
handle_completion(th); | |
} | |
} | |
// Write output coverage for unfinished calls. | |
// 即使超时未完成,也要收集覆盖率和写输出,便于后续分析 | |
if (running > 0) { | |
for (int i = 0; i < kMaxThreads; i++) { | |
thread_t* th = &threads[i]; | |
if (th->executing) { | |
if (cover_collection_required()) | |
cover_collect(&th->cov); | |
write_call_output(th, false); | |
} | |
} | |
} | |
} | |
// 写 extra output /extra coverage(并避免被 timeout 杀死前来不及写) | |
write_extra_output(); | |
if (flag_extra_coverage) { | |
// Check for new extra coverage in small intervals to avoid situation | |
// that we were killed on timeout before we write any. | |
// Check for extra coverage is very cheap, effectively a memory load. | |
const uint64 kSleepMs = 100; | |
for (uint64 i = 0; i < prog_extra_cover_timeout / kSleepMs && | |
output_data->completed.load(std::memory_order_relaxed) < kMaxCalls; | |
i++) { | |
sleep_ms(kSleepMs); | |
write_extra_output(); | |
} | |
} | |
} |
# ShmemBuilder
output_builder 是一个 optional 的 ShmemBuilder 类型的变量, ShmemBuilder 类对 output_data 进行了一层封装,他把 “输出共享内存” 伪装成一个可追加的 FlatBuffer / 字节流构建器。通过该封装既能在共享内存里分配空间,又能按 FlatBuffer 的写法把结果序列化进去,并且支持 “断点续写”。
ShmemBuilder(OutputData* data, size_t size, bool store_size) | |
// 继承自两个类,ShmemAllocator 负责分配内存,FlatBufferBuilder 负责构建 flatbuffers 输出消息 | |
: ShmemAllocator(data + 1, size - sizeof(*data)), | |
FlatBufferBuilder(size - sizeof(*data), this) | |
{ | |
// 是否把 output_size 写到头部(snapshot 模式下不写,因为大小是固定的已知的) | |
if (store_size) | |
data->size.store(size, std::memory_order_relaxed); | |
// 记录已经使用的内存大小,初始为 0,用于支持 “从上次写到的位置继续写” | |
size_t consumed = data->consumed.load(std::memory_order_relaxed); | |
if (consumed >= size - sizeof(*data)) | |
failmsg("ShmemBuilder: too large output offset", "size=%zd consumed=%zd", size, consumed); | |
if (consumed) | |
// 如果 consumed 不为 0,让 FlatBufferBuilder 的内部 buffer 先 “跳过” 这些字节 | |
// 后续通过 builder 追加的数据就会从 consumed 位置开始写,而不会覆盖之前的数据 | |
FlatBufferBuilder::buf_.make_space(consumed); | |
} | |
}; |
# read_input
read_input 是 executor 的 “字节码解码器” 之一。它从 input_data 的当前位置读取一个变长整数(varint),再做 ZigZag 还原成有符号整数(但用 uint64 承载),并根据 peek 决定是否更新指针:
peek=false:正常读取,会推进*input_posp。peek=true:窥探,不推进*input_posp,只返回值(用于 “先看看下一项是什么”)。
变长整数的设计也很巧妙,每个字节中只有 0~7 bit 是有效位,最高位用来编码是否结束。 64-bit varint 最多需要 10 个字节(10×7=70 bits),所以 maxLen 限制在 10, shift 每次加 7。
uint64 read_input(uint8** input_posp, bool peek) | |
{ | |
uint64 v = 0; | |
unsigned shift = 0; | |
uint8* input_pos = *input_posp; | |
// 变长解码循环 | |
for (int i = 0;; i++, shift += 7) { | |
const int maxLen = 10; | |
if (i == maxLen) | |
failmsg("varint overflow", "pos=%zu", (size_t)(*input_posp - input_data)); | |
if (input_pos >= input_data + kMaxInput) | |
failmsg("input command overflows input", "pos=%p: [%p:%p)", | |
input_pos, input_data, input_data + kMaxInput); | |
uint8 b = *input_pos++; | |
v |= uint64(b & 0x7f) << shift; | |
// 最高位为 0 表示结束 | |
if (b < 0x80) { | |
if (i == maxLen - 1 && b > 1) | |
failmsg("varint overflow", "pos=%zu", (size_t)(*input_posp - input_data)); | |
break; | |
} | |
} | |
// 有符号解码 | |
if (v & 1) | |
v = ~(v >> 1); // 负数,用补码表示 | |
else | |
v = v >> 1; // 正数 | |
// 更新输入位置指针 | |
if (!peek) | |
*input_posp = input_pos; | |
return v; | |
} |
# schedule_call
为一次 syscall(program 的一个 call)挑选 / 创建一个可用 worker 线程,把执行所需的元数据和参数塞进 thread_t ,重置同步 / 覆盖率状态,然后把线程 “唤醒” 去执行,并把全局 running 计数加一。
schedule_call 中采用懒创建线程,具体方法为:按顺序从 threads 线程池中依次查询是否空闲,如果空闲则用该线程执行;如果前面都不空闲,且此时 threads 池没有达到上限,则创建一个新的线程来执行 syscall。
thread_t* schedule_call(int call_index, int call_num, uint64 copyout_index, uint64 num_args, uint64* args, uint8* pos, call_props_t call_props) | |
{ | |
// 找一个 “空闲线程槽” 来跑这个 call(必要时创建线程) | |
int i = 0; | |
for (; i < kMaxThreads; i++) { | |
thread_t* th = &threads[i]; //threads [] 是一个固定大小线程池 | |
// 懒创建线程,只有用到时才创建 | |
if (!th->created) | |
// 创建线程,并传入是否需要覆盖率收集参数 | |
thread_create(th, i, cover_collection_required()); | |
// 如果 done 置位但 executing 仍为 true,说明线程完成了 syscall 但主线程还没处理 completion: | |
// 就先 handle_completion (th) 把上一个 call 的结果 / 输出 / 覆盖写出去并清状态。 | |
// 然后这个线程槽才能安全复用。 | |
if (event_isset(&th->done)) { | |
if (th->executing) | |
handle_completion(th); | |
break; | |
} | |
} | |
if (i == kMaxThreads) | |
exitf("out of threads"); | |
thread_t* th = &threads[i]; | |
// 强状态检查,确保线程处于 “空闲可用” 状态 | |
if (event_isset(&th->ready) || !event_isset(&th->done) || th->executing) | |
exitf("bad thread state in schedule: ready=%d done=%d executing=%d", | |
event_isset(&th->ready), event_isset(&th->done), th->executing); | |
// 记录最后一次派发的线程 | |
last_scheduled = th; | |
// 把 copyout 信息挂到 thread 上,便于 syscall 执行完后做 copyout | |
th->copyout_pos = pos; | |
th->copyout_index = copyout_index; | |
// 把 done 复位为未完成状态,表示准备执行新 syscall | |
event_reset(&th->done); | |
// We do this both right before execute_syscall in the thread and here because: | |
// the former is useful to reset all unrelated coverage from our syscalls (e.g. futex in event_wait), | |
// while the reset here is useful to avoid the following scenario that the fuzzer was able to trigger. | |
// If the test program contains seccomp syscall that kills the worker thread on the next syscall, | |
// then it won't receive this next syscall and won't do cover_reset. If we are collecting comparions | |
// then we've already transformed comparison data from the previous syscall into rpc::ComparisonRaw | |
// in write_comparisons. That data is still in the buffer. The first word of rpc::ComparisonRaw is PC | |
// which overlaps with comparison type in kernel exposed records. As the result write_comparisons | |
// that will try to write out data from unfinished syscalls will see these rpc::ComparisonRaw records, | |
// mis-interpret PC as type, and fail as: SYZFAIL: invalid kcov comp type (type=ffffffff8100b4e0). | |
if (flag_coverage) | |
cover_reset(&th->cov); | |
// 填充 thread_t,把要执行的 syscall 描述写进去 | |
th->executing = true; | |
th->call_index = call_index; | |
th->call_num = call_num; | |
th->num_args = num_args; | |
th->call_props = call_props; | |
for (int i = 0; i < kMaxArgs; i++) | |
th->args[i] = args[i]; | |
// 通知 worker 线程,可以开始执行 execute_call () 了 | |
event_set(&th->ready); | |
// 更新全局正在运行的 syscall 数 | |
running++; | |
return th; | |
} |
# thread_create
在默认情况下 flag_threaded 为真,即所有 syscall 其实都是在线程中执行的,syscall 之间存在交错。
void thread_create(thread_t* th, int id, bool need_coverage)
{
// 创建实际执行 syscall 的线程
th->created = true;
th->id = id;
th->executing = false;
// Lazily set up coverage collection.
// It is assumed that actually it's already initialized - with a few rare exceptions.
if (need_coverage) {
if (!th->cov.fd)
exitf("out of opened kcov threads");
thread_mmap_cover(th);
}
// 初始化两个event,用于与执行线程同步状态
event_init(&th->ready);
event_init(&th->done);
event_set(&th->done);
if (flag_threaded)
thread_start(worker_thread, th);
}
# thread_start
static void thread_start(void* (*fn)(void*), void* arg)
{
pthread_t th;
pthread_attr_t attr;
pthread_attr_init(&attr);
pthread_attr_setstacksize(&attr, 128 << 10); // 显式设置栈大小为 128KB
// Clone can fail spuriously with EAGAIN if there is a concurrent execve in progress.
// (see linux kernel commit 498052bba55ec). But it can also be a true limit imposed by cgroups.
// In one case we want to retry infinitely, in another -- fail immidiately...
// 最多尝试 100 次创建线程
int i = 0;
for (; i < 100; i++) {
// 创建的线程将执行函数 fn(worker_thread)
if (pthread_create(&th, &attr, fn, arg) == 0) {
pthread_attr_destroy(&attr);
return;
}
if (errno == EAGAIN) { // 失败重试
usleep(50);
continue;
}
break;
}
exitf("pthread_create failed");
}
# worker_thread
void* worker_thread(void* arg)
{
// 每个 worker 线程对应一个 thread_t
thread_t* th = (thread_t*)arg;
current_thread = th;
// worker 永不退出, 每次循环执行一个 syscall
for (bool first = true;; first = false) {
event_wait(&th->ready); // 睡眠等待 ready 事件
event_reset(&th->ready); // 消费 ready,防止下次循环误触发
// Setup coverage only after receiving the first ready event
// because in snapshot mode we don't know coverage mode for precreated threads.
if (first && cover_collection_required()) // 第一次执行时启用 coverage
cover_enable(&th->cov, flag_comparisons, false);
execute_call(th); // 执行一次 syscall
event_set(&th->done); // 同步状态为 done
}
return 0;
}
# execute_call
execute_call 执行一次 syscall(或伪 syscall),可选地启用故障注入 / 重复执行 / 覆盖率收集,然后把结果(res/errno/coverage/ 是否注入成功等)写回 thread_t 供主线程的 handle_completion() 后续序列化输出。
void execute_call(thread_t* th) | |
{ | |
// 取 syscall 描述并打印调用日志 | |
const call_t* call = &syscalls[th->call_num]; | |
debug("#%d [%llums] -> %s(", | |
th->id, current_time_ms() - start_time_ms, call->name); | |
for (int i = 0; i < th->num_args; i++) { | |
if (i != 0) | |
debug(", "); | |
debug("0x%llx", (uint64)th->args[i]); | |
} | |
debug(")\n"); | |
// 可选:注入故障 | |
int fail_fd = -1; | |
th->soft_fail_state = false; | |
if (th->call_props.fail_nth > 0) { | |
if (th->call_props.rerun > 0) | |
fail("both fault injection and rerun are enabled for the same call"); | |
fail_fd = inject_fault(th->call_props.fail_nth); | |
th->soft_fail_state = true; | |
} | |
// 重置覆盖率收集状态 | |
if (flag_coverage) | |
cover_reset(&th->cov); | |
// For pseudo-syscalls and user-space functions NONFAILING can abort before assigning to th->res. | |
// Arrange for res = -1 and errno = EFAULT result for such case. | |
// 设置默认 res/errno | |
th->res = -1; | |
errno = EFAULT; | |
// 用 NONFAILING 是希望执行器尽可能不被单个 call 弄死,将崩溃转成错误返回 | |
//execute_syscall 里面用 syscall () 真正执行系统调用 | |
NONFAILING(th->res = execute_syscall(call, th->args)); | |
th->reserrno = errno; | |
// 伪 syscall 可能 “行为不规范”,所以这里修正一下 | |
// 伪 syscall 指的是那些不直接对应内核 syscall 的函数,比如 syz_open_dev、syz_emit_ethernet 等 | |
// 这些 syscall 的执行不是通过内核 syscall () 实现的,而是通过用户态代码模拟实现的 | |
if ((th->res == -1 && th->reserrno == 0) || call->attrs.ignore_return) | |
th->reserrno = EINVAL; | |
// Reset the flag before the first possible fail(). | |
// 在任何可能触发 fail () 的点之前清掉 soft_fail_state, | |
// 避免之后把真正的执行器失败误判为 “故障注入导致的软失败”。 | |
th->soft_fail_state = false; | |
// 收集覆盖率 | |
if (flag_coverage) | |
cover_collect(&th->cov); | |
// 判断故障注入是否真的命中,故障注入不是 100% 生效,尤其在不同内核配置 / 路径下 | |
th->fault_injected = false; | |
if (th->call_props.fail_nth > 0) | |
th->fault_injected = fault_injected(fail_fd); | |
// If required, run the syscall some more times. | |
// But let's still return res, errno and coverage from the first execution. | |
// 根据 call_props.rerun 决定是否重跑 syscall 多次 | |
for (int i = 0; i < th->call_props.rerun; i++) | |
NONFAILING(execute_syscall(call, th->args)); | |
// 打印调用结果日志 | |
debug("#%d [%llums] <- %s=0x%llx", | |
th->id, current_time_ms() - start_time_ms, call->name, (uint64)th->res); | |
if (th->res == (intptr_t)-1) | |
debug(" errno=%d", th->reserrno); | |
if (flag_coverage) | |
debug(" cover=%u", th->cov.size); | |
if (th->call_props.fail_nth > 0) | |
debug(" fault=%d", th->fault_injected); | |
if (th->call_props.rerun > 0) | |
debug(" rerun=%d", th->call_props.rerun); | |
debug("\n"); | |
} |
# execute_syscall
实际执行 syscall 和伪 syscall。
static intptr_t execute_syscall(const call_t* c, intptr_t a[kMaxArgs]) | |
{ | |
// 伪 syscall 执行 | |
if (c->call) | |
return c->call(a[0], a[1], a[2], a[3], a[4], a[5], a[6], a[7], a[8]); | |
//syscall 执行 | |
return syscall(c->sys_nr, a[0], a[1], a[2], a[3], a[4], a[5]); | |
} |
# handle_completion
当某个 worker 线程把 syscall 跑完(done 置位)后,主线程在这里把结果从线程上下文搬运到输出共享内存(copyout + write_call_output + extra),并把线程恢复为可复用状态,同时维护全局 running 计数。
void handle_completion(thread_t* th) | |
{ | |
// 状态机断言:完成时必须满足 ready=0, done=1, executing=1 | |
if (event_isset(&th->ready) || !event_isset(&th->done) || !th->executing) | |
exitf("bad thread state in completion: ready=%d done=%d executing=%d", | |
event_isset(&th->ready), event_isset(&th->done), th->executing); | |
// 成功返回才做 copyout,把内核写回的内存数据读出来保存 | |
if (th->res != (intptr_t)-1) | |
copyout_call_results(th); | |
// 写本 call 的输出记录到 output shmem:结果、errno、signal、cover 等 | |
write_call_output(th, true); | |
// 写 extra output:把额外覆盖 /extra signal 等追加进去 | |
write_extra_output(); | |
// 把线程标记为空闲,并维护 running 计数 | |
th->executing = false; | |
running--; | |
// 长期运行中可能出现计数异常,这时打印所有线程状态并退出 | |
if (running < 0) { | |
// This fires periodically for the past 2 years (see issue #502). | |
fprintf(stderr, "running=%d completed=%d flag_threaded=%d current=%d\n", | |
running, completed, flag_threaded, th->id); | |
for (int i = 0; i < kMaxThreads; i++) { | |
thread_t* th1 = &threads[i]; | |
fprintf(stderr, "th #%2d: created=%d executing=%d" | |
" ready=%d done=%d call_index=%d res=%lld reserrno=%d\n", | |
i, th1->created, th1->executing, | |
event_isset(&th1->ready), event_isset(&th1->done), | |
th1->call_index, (uint64)th1->res, th1->reserrno); | |
} | |
exitf("negative running"); | |
} | |
} |
# write_call_output
把一个 call 的完成状态编码成 RPC 元信息(Executed/Finished/Blocked/FaultInjected + errno + 是否发送全量 signal),并连同 coverage 一起交给 write_output 写入共享输出缓冲。
void write_call_output(thread_t* th, bool finished) | |
{ | |
// 设置默认错误码 | |
uint32 reserrno = ENOSYS; | |
rpc::CallFlag flags = rpc::CallFlag::Executed; | |
// 如果完成了,而且 “不是最后一次调度的 call”,标记 Blocked | |
// Blocked 指的是发生了时序错乱,后面派发的 call 先完成了 | |
if (finished && th != last_scheduled) | |
flags |= rpc::CallFlag::Blocked; | |
// 只有真正完成的 call 才写实际结果和错误码 | |
if (finished) { | |
reserrno = th->res != -1 ? 0 : th->reserrno; | |
flags |= rpc::CallFlag::Finished; | |
if (th->fault_injected) | |
flags |= rpc::CallFlag::FaultInjected; | |
} | |
// 是否要求把该 call 的 “全量 signal” 都输出还是只输出新出现的 signal | |
bool all_signal = th->call_index < 64 ? (all_call_signal & (1ull << th->call_index)) : false; | |
// 真正写输出,交给 write_output 序列化到共享内存 | |
write_output(th->call_index, &th->cov, flags, reserrno, all_signal); | |
} |
# write_output
它把一次 call 的 coverage/signal/comparisons 这些 “可变长数据” 写进 output 共享内存(通过 output_builder 追加构建),再写一个 CallInfo 记录(flags/errno/ 各段偏移),最后用原子 store 把这条记录发布到 output_data->calls[slot] 并递增 completed 。
void write_output(int index, cover_t* cov, rpc::CallFlag flags, uint32 error, bool all_signal) | |
{ | |
// 对 coverage 缓冲做访问保护 | |
CoverAccessScope scope(cov); | |
// 准备 FlatBuffers 构建器 | |
auto& fbb = *output_builder; | |
// 写本次输出之前 builder 已经消耗了多少字节,给调试留的 | |
const uint32 start_size = output_builder->GetSize(); | |
(void)start_size; | |
// 三种可选输出:signal /cover/comparisons(互斥) | |
// 默认收集 signal | |
uint32 signal_off = 0; // 信号 | |
uint32 cover_off = 0; // 覆盖率 | |
uint32 comps_off = 0; // 比较操作数 | |
if (flag_comparisons) { | |
comps_off = write_comparisons(fbb, cov); | |
} else { | |
if (flag_collect_signal) { | |
if (is_kernel_64_bit) | |
signal_off = write_signal<uint64>(fbb, index, cov, all_signal); | |
else | |
signal_off = write_signal<uint32>(fbb, index, cov, all_signal); | |
} | |
if (flag_collect_cover) { | |
if (is_kernel_64_bit) | |
cover_off = write_cover<uint64>(fbb, cov); | |
else | |
cover_off = write_cover<uint32>(fbb, cov); | |
} | |
} | |
// 写一个 “索引记录”,指向上面写的 blobs | |
rpc::CallInfoRawBuilder builder(*output_builder); | |
if (cov->overflow) | |
flags |= rpc::CallFlag::CoverageOverflow; | |
builder.add_flags(flags); | |
builder.add_error(error); | |
if (signal_off) | |
builder.add_signal(signal_off); | |
if (cover_off) | |
builder.add_cover(cover_off); | |
if (comps_off) | |
builder.add_comps(comps_off); | |
auto off = builder.Finish(); | |
// 发布到 calls [slot]:两阶段提交,先写数据,再更新指针和计数 | |
uint32 slot = output_data->completed.load(std::memory_order_relaxed); // 原子性更新共享内存 | |
if (slot >= kMaxCalls) | |
failmsg("too many calls in output", "slot=%d", slot); | |
auto& call = output_data->calls[slot]; | |
call.index = index; | |
call.offset = off; | |
output_data->consumed.store(output_builder->GetSize(), std::memory_order_release); | |
output_data->completed.store(slot + 1, std::memory_order_release); | |
debug_verbose("out #%u: index=%u errno=%d flags=0x%x total_size=%u\n", | |
slot + 1, index, error, static_cast<unsigned>(flags), call.data_size - start_size); | |
} |
# write_signal
把一次 syscall 的 coverage 记录(一串 PC/edge id)转换成 “反馈信号 signal” 并写进输出 FlatBuffer。相比 coverage,signal 是一种更稳定的指标,能更有效的指导变异方向。
template <typename cover_data_t> | |
uint32 write_signal(flatbuffers::FlatBufferBuilder& fbb, int index, cover_t* cov, bool all) | |
{ | |
// Write out feedback signals. | |
// Currently it is code edges computed as xor of two subsequent basic block PCs. | |
fbb.StartVector(0, sizeof(uint64)); | |
cover_data_t* cover_data = (cover_data_t*)(cov->data + cov->data_offset); | |
if ((char*)(cover_data + cov->size) > cov->data_end) | |
failmsg("too much cover", "cov=%u", cov->size); | |
uint32 nsig = 0; | |
cover_data_t prev_pc = 0; | |
bool prev_filter = true; | |
// 逐条取 PC,生成 signal | |
for (uint32 i = 0; i < cov->size; i++) { | |
cover_data_t pc = cover_data[i] + cov->pc_offset; | |
uint64 sig = pc; | |
if (use_cover_edges) { | |
// Only hash the lower 12 bits so the hash is independent of any module offsets. | |
// 把 signal 转成边覆盖形式:当前 PC 和前一个 PC 的异或 | |
// 只用低 12 位参与哈希,目的是让 signal 对模块加载偏移不敏感 | |
const uint64 mask = (1 << 12) - 1; | |
sig ^= hash(prev_pc & mask) & mask; | |
} | |
bool filter = coverage_filter(pc); // 检查 pc 是否在过滤器内 | |
// Ignore the edge only if both current and previous PCs are filtered out | |
// to capture all incoming and outcoming edges into the interesting code. | |
// 只有当前和前一个都 “不感兴趣” 时,才忽略这个 edge/signal | |
// 进入 / 离开 感兴趣区域的边也要保留(对探索路径很重要) | |
bool ignore = !filter && !prev_filter; | |
prev_pc = pc; | |
prev_filter = filter; | |
// 去重 | |
if (ignore || dedup(index, sig)) | |
continue; | |
// 如果不要求 all_signal(全量),就把 “已经在 max_signal 集合里的信号” 丢掉 | |
if (!all && max_signal && max_signal->Contains(sig)) | |
continue; | |
// 写入 Flatbuffer | |
fbb.PushElement(uint64(sig)); | |
nsig++; | |
} | |
// 结束 Flatbuffer 向量构建 | |
return fbb.EndVector(nsig); | |
} |
# 向 manager 发送结果
当 worker 进程执行完所有 syscall 后,或者被超时强行杀掉后,子进程退出,此时 loop 中会通过 reply_execute(0) 来通知 runner 执行结束了,runner 在 Loop 循环中会通过 proc->Ready(select, now, requests_.empty()); 来检测是否有 worker 执行完成,如果有,获取结果并向 manager 发送。
# Proc.Ready
负责三件事:
- 超时监视,如果超时则重启子进程
- 读 stderr 日志
- 读
resp_pipe_上的协议回复(prog 完成通知 / 握手回复)
void Ready(Select& select, uint64 now, bool out_of_requests) | |
{ | |
// 只在这两种 “正在等待子进程干活” 的状态下做超时检测。 | |
if (state_ == State::Handshaking || state_ == State::Executing) { | |
// Check if the subprocess has hung. | |
#if SYZ_EXECUTOR_USES_FORK_SERVER | |
// Child process has an internal timeout and protects against most hangs when | |
// fork server is enabled, so we use quite large timeout. Child process can be slow | |
// due to global locks in namespaces and other things, so let's better wait than | |
// report false misleading crashes. | |
//fork server 模式下,子进程内部有超时保护,且可能因为命名空间等全局锁而变慢, | |
uint64 timeout = 3 * ProgramTimeoutMs(); | |
#else | |
uint64 timeout = ProgramTimeoutMs(); | |
#endif | |
// Sandbox setup can take significant time. | |
if (state_ == State::Handshaking) | |
// 握手阶段的 “慢” 更常见,所以单独放宽,避免频繁重启导致永远握手不成功 | |
timeout = 60 * 1000 * slowdown_; | |
if (now > exec_start_ + timeout) { | |
Restart(); // 超时,强行重启子进程 | |
return; | |
} | |
} | |
// 处理子进程 stderr/log 输出 | |
if (select.Ready(stdout_pipe_) && !ReadOutput()) { | |
#if SYZ_EXECUTOR_USES_FORK_SERVER | |
// In non-forking mode the subprocess exits after test execution | |
// and the pipe read fails with EOF, so we rely on the resp_pipe_ instead. | |
Restart(); | |
return; | |
#endif | |
} | |
// 读取协议响应(执行完成 / 结果就靠它) | |
if (select.Ready(resp_pipe_) && !ReadResponse(out_of_requests)) { | |
Restart(); // 读取失败或 EOF,重启 | |
return; | |
} | |
return; | |
} |
# ReadResponse
从 resp_pipe_ 读取 worker 的执行结果(成功 / 失败),并根据当前的状态判断回复的是握手结果还是执行结果,并做不同的处理。
bool ReadResponse(bool out_of_requests) | |
{ | |
uint32 status; | |
ssize_t n; | |
// 从响应管道读取状态码 | |
while ((n = read(resp_pipe_, &status, sizeof(status))) == -1) { | |
if (errno != EINTR && errno != EAGAIN) | |
break; | |
} | |
if (n == 0) { // EOF,子进程可能崩溃 | |
debug("proc %d: response pipe EOF\n", id_); | |
return false; | |
} | |
if (n != sizeof(status)) | |
failmsg("proc resp pipe read failed", "n=%zd", n); | |
// 根据当前状态处理响应 | |
if (state_ == State::Handshaking) { | |
debug("proc %d: got handshake reply\n", id_); | |
// 收到握手回复,转为空闲状态 | |
ChangeState(State::Idle); | |
// 握手完成,立即开始执行之前保存的请求 | |
// 对应 Execute (rpc::ExecRequestRawT& msg) 中 state_ == State::Started 的情况 | |
Execute(); | |
} else if (state_ == State::Executing) { | |
// 收到执行完成回复 | |
debug("proc %d: got execute reply\n", id_); | |
HandleCompletion(status); // 处理执行结果 | |
if (out_of_requests) | |
wait_start_ = current_time_ms(); // 记录空闲开始时间 | |
} else { | |
debug("got data on response pipe in wrong state %d\n", state_); | |
return false; | |
} | |
return true; | |
} |
# HandleCompletion
把 “exec 子进程已经完成” 的状态转成一条发给 manager 的 RPC 响应。它干的事可以概括成四步:
- 计算耗时、准备输入指针(用于解析 program header)
- (可选)把 stderr 输出 / 退出码拼进
output_(ReturnOutput 模式) - 从
resp_shmem_(resp_mem_)里把本轮写好的 call 输出 “封包” 成消息data,发给 manager - 清理状态,回到 Idle,必要时重启 exec 子进程
void HandleCompletion(uint32 status, bool hanged = false) | |
{ | |
// 必须有正在执行的 msg_ | |
if (!msg_) | |
fail("don't have executed msg"); | |
// Note: if the child process crashed during handshake and the request has ReturnError flag, | |
// we have not started executing the request yet. | |
// 计算本次执行耗时(纳秒单位) | |
uint64 elapsed = (current_time_ms() - exec_start_) * 1000 * 1000; | |
// 把 input_data 指到本次 program 数据,便于后面解析 | |
uint8* prog_data = msg_->data.data(); | |
input_data = prog_data; | |
std::vector<uint8_t>* output = nullptr; | |
// ReturnOutput 模式:需要返回 stderr / 日志,准备 output 指针并追加退出码 | |
if (IsSet(msg_->flags, rpc::RequestFlag::ReturnOutput)) { | |
output = &output_; | |
if (status) { | |
char tmp[128]; | |
snprintf(tmp, sizeof(tmp), "\nprocess exited with status %d\n", status); | |
output_.insert(output_.end(), tmp, tmp + strlen(tmp)); | |
} | |
} | |
// 只对 Program 类型从 program header 里读 “call 数” | |
uint32 num_calls = 0; | |
if (msg_->type == rpc::RequestType::Program) | |
num_calls = read_input(&prog_data); | |
// 核心:从共享内存把 call 输出封包成 RPC 回复 | |
auto data = finish_output(resp_mem_, id_, msg_->id, num_calls, elapsed, freshness_++, status, hanged, output); | |
// 发送给 manager | |
conn_.Send(data.data(), data.size()); | |
// 清理共享内存与请求状态,回到 Idle | |
resp_mem_->Reset(); | |
msg_.reset(); | |
output_.clear(); | |
debug_output_pos_ = 0; | |
ChangeState(State::Idle); | |
#if !SYZ_EXECUTOR_USES_FORK_SERVER | |
if (process_) | |
Restart(); | |
#endif | |
} |
# finish_output
将 worker 子进程执行结果封装成最终发送给 manager 的消息
flatbuffers::span<uint8_t> finish_output(OutputData* output, int proc_id, uint64 req_id, uint32 num_calls, uint64 elapsed, | |
uint64 freshness, uint32 status, bool hanged, const std::vector<uint8_t>* process_output) | |
{ | |
// In snapshot mode the output size is fixed and output_size is always initialized, so use it. | |
// 快照模式:使用固定大小 | |
int out_size = flag_snapshot ? output_size : output->size.load(std::memory_order_relaxed) ? | |
: kMaxOutput; // 否则:从共享内存读取或使用默认值 | |
uint32 completed = output->completed.load(std::memory_order_relaxed); | |
// Executor 子进程通过 write_output 原子递增这个值 | |
// 表示实际完成并写入结果的系统调用数量 | |
completed = std::min(completed, kMaxCalls); | |
debug("handle completion: completed=%u output_size=%u\n", completed, out_size); | |
// 初始化 FlatBuffers 构建器,不更新 size (仅读取) | |
ShmemBuilder fbb(output, out_size, false); | |
// 创建空的 “调用信息” 占位符,错误码 998 表示 "未执行" | |
auto empty_call = rpc::CreateCallInfoRawDirect(fbb, rpc::CallFlag::NONE, 998); | |
std::vector<flatbuffers::Offset<rpc::CallInfoRaw>> calls(num_calls, empty_call); | |
std::vector<flatbuffers::Offset<rpc::CallInfoRaw>> extra; // 额外覆盖率 | |
// 填充实际的调用结果 | |
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < completed; i++) { | |
const auto& call = output->calls[i]; | |
// 特殊情况:额外覆盖率(index = -1) | |
if (call.index == -1) { | |
extra.push_back(call.offset); | |
continue; | |
} | |
// 验证调用索引和偏移量的合法性 | |
if (call.index < 0 || call.index >= static_cast<int>(num_calls) || call.offset.o > kMaxOutput) { | |
debug("bad call index/offset: proc=%d req=%llu call=%d/%d completed=%d offset=%u", | |
proc_id, req_id, call.index, num_calls, | |
completed, call.offset.o); | |
continue; // 跳过非法数据 | |
} | |
// 将实际结果填充到对应位置 | |
calls[call.index] = call.offset; | |
} | |
// 构建 Prog 信息对象 | |
auto prog_info_off = rpc::CreateProgInfoRawDirect(fbb, &calls, &extra, 0, elapsed, freshness); | |
// 处理错误信息(Executor 子进程异常退出) | |
flatbuffers::Offset<flatbuffers::String> error_off = 0; | |
if (status == kFailStatus) | |
error_off = fbb.CreateString("process failed"); | |
// If the request wrote binary result (currently glob requests do this), use it instead of the output. | |
// 处理二进制结果(特殊情况) | |
auto output_off = output->result_offset.load(std::memory_order_relaxed); | |
if (output_off.IsNull() && process_output) | |
output_off = fbb.CreateVector(*process_output); | |
// 构建最终的 ExecResult 消息 | |
auto exec_off = rpc::CreateExecResultRaw(fbb, req_id, proc_id, output_off, hanged, error_off, prog_info_off); | |
// 封装为 ExecutorMessage 并返回 | |
auto msg_off = rpc::CreateExecutorMessageRaw(fbb, | |
rpc::ExecutorMessagesRaw::ExecResult, // 消息类型 | |
flatbuffers::Offset<void>(exec_off.o) // 消息内容 | |
); | |
fbb.FinishSizePrefixed(msg_off); // 完成序列化(添加大小前缀) | |
return fbb.GetBufferSpan(); // 返回序列化后的字节数组 | |
} |